1) When doing an assessment on a client’s eyes the very first thing that a nurse should look at is?
A. Eye internal structures
B. Eye external structures
C. The pupils reactivity to light
D. Color of the irises of the eye
2) While the nurse is inspecting the throat of a client with a tongue blade, the client begins to gag. What does this response indicate to the nurse?
A. The client is nauseated.
B. The client has nerve damage to his tongue.
C. The client has a functioning response.
D. The client has a malfunctioning response
3) During the health history, a client begins to talk about her dog and the trouble she is having housebreaking the new pet. To help the client return to the health interview, the nurse could use the communication skill:
A. Listening
B. Reflecting
C. Questioning
D. Focusing
4) After inspecting a client’s abdomen, which assessment technique should the nurse use next?
A. Light Palpation
B. Percussion
C. Auscultation
D. Deep Palpation
5) Nurse Tara asks her client Farhan to clench his jaw as she continues to palpate his head. When she asks him to do this what is Nurse Tara most likely trying to palpate?
A. Faran’s submandibular joint
B. Farhan’s submental joint
C. Farhan’s temporomandibular joint
D. Faran’s temporal artery
6) The nurse is planning to palpate a client’s bladder. Which area of the abdomen should this palpation be done?
A. Hypogastric region
B. Right hypochondriac region
C. Right Lower Quadrant
D. Left lumbar region
7) A 70-year-old male client comes into the clinic with weight loss and difficulty swallowing. Which of the following should the nurse document for this client?
A. Odynophagia
B. Bulimia
C. Dysphagia
D. Aphasia
8) A 15-year-old high school student came to the clinic with a 1-day history of nausea and anorexia. He describes the pain as generalized yesterday, but today it has localized to the right lower quadrant. You palpate the left lower quadrant and the patient experiences pain in the right lower quadrant. What is the name of this sign?
A. Murphy’s sign
B. Psoas sign
C. Grey Turner’s sign
D. Rovsing’s sign
9) During eye assessment when you asked the patient to follow your finger or pencil as you move it in toward the bridge of the nose. Which of the following test you are performing?
A. Visual acuity
B. Visual Fields by Confrontation
C. Test for convergence
D. Visual fields
10) A nurse doing her assessment proceeds to palpate a client’s frontal and maxillary sinuses. What should she make sure she checks for?
A. Tactile signs of carcinoma
B. Swelling
C. Lesions
D. Tenderness
11) A nurse would use either a Snelling chart or the finger wiggle test to assess a client’s what?
A. Hearing
B. Vision
C. Consensual light reflex
D. Bone conduction
12) During assessment of pharynx you as the client to say “Ah” and uvula and soft palate rise centrally. It determines the function of which cranial nerve:
A. Spinal accessory
B. Vagus
C. Trochlear
D. Trigeminal
13) During the assessment of a client, the nurse gently touches the tip of a sterile cotton swab in the client’s eye. Which of the following would be considered an expected response for the client to make?
A. Begin sneezing.
B. Blink.
C. Scream in pain.
D. Swat the nurse’s hand away.
14) If assessing a client for kidney tenderness, where would you begin?
A. External Oblique Angle
B. Left Upper Quadrant
C. Right Upper Quadrant
D. Costovertebral Angle
15) The three things a nurse needs to check for when doing an examination on the eyes regarding the external structures is?
A. Eyelash texture, shape of eyes, redness
B. Shape of eyes, pupils reactivity, iris’s color
C. Drainage, possible tumors, irritation
D. Eyelash distribution, coloring, drainage
16) A 40-year-old female came for evaluation of abdominal pain. She stated that it is worse after eating, especially if she has a meal that is spicy or high in fat. She has taken antacids, but they have not helped the pain. After examining her abdomen, you strongly suspect cholecystitis. Which sign on examination increases your suspicion for this diagnosis?
A. Murphy’s sign
B. Psoas sign
C. Grey Turner’s sign
D. Rovsing’s sign
17) During the percussion of a client’s abdomen, the nurse hears a loud high-pitched drum like tone. The nurse would document this sound as being:
A. Resonance
B. Tympany
C. Hyper-resonance
D. Flatness
18) What could the nurse assess based solely on the way the client walks into the room?
A. Signs of illness, well nourished
B. Dress and signs of illness
C. Gender and age
D. Gait and posture
19) Which of the following is a clinical manifestation of Bell’s palsy?
A. Asymmetry of the mouth
B. Asymmetry of the entire side of the face
C. Asymmetry of the lower face
D. Involuntary movements of the face
20) The nurse notices that a client walks with a limp and has long legs. Which of the following aspects of the general survey is this nurse assessing?
A. Physical appearance
B. Behavior
C. Mental status
D. Mobility
21) Test for shifting dullness is performed to assess:
A. Liver abscess
B. Ascites
C. Cholecystitis
D. Peritonitis
22) When a nurse performing the eye examinations, which piece of equipment does she/he use to inspect the eye structures?
A. Ultrasonic stethoscope
B. Sphygmomanometer
C. Ophthalmoscope
D. Otoscope
23) The normal liver span of an adult is:
A. 7-12 cm
B. 5-12 cm
C. 6-12 cm
D. 4-12 cm
24) A client comes into the clinic for a routine breast and axilla exam. Which assessment technique does the nurse use first during this examination?
A. Palpation
B. Auscultation
C. Inspection
D. Percussion
25) The clinic is sponsoring a client education session for breast cancer awareness month. Which of the following considerations should be included to support cultural differences about breast health?
A. Refer all clients to the American Cancer Society if they have questions.
B. Inform all about the low-cost breast cancer screening program…
C. A:
D. Encourage all females to increase their intake of vitamins A and E
26) Grade +2 pitting edema is:
A. 4 mm deep
B. 6 mm deep
C. 2 mm deep
D. 8 mm deep
27) The nurse is going to assess a client’s blood pressure. To do this, the nurse will need to have:
A. A stethoscope and sphygmomanometer
B. A tongue blade and tuning fork
C. A flashlight and gloves
D. A stethoscope and thermometer
28) The clinic is sponsoring a client education session for breast cancer awareness month. Which of the following considerations should be included to support cultural differences about breast health?
A. Refer all clients to the American Cancer Society if they have questions.
B. Encourage all females to increase their intake of vitamins A and E.
C. Inform all about the low-cost breast cancer screening program.
D. Encourage all females to complete monthly breast exams
29) After auscultating the bowel sounds of a client, the nurse realizes the sounds were long. Which of the following would be appropriate for the nurse to use to document this finding?
A. Intensity
B. Pitch
C. Quality
D. Duration
30) During the physical assessment of Mr. Ahsan’s skin, the nurse observed that Mr. Ahsan’s skin color is pale, the nurse expect that Mr. Ahsan may has:
A. Jaundice
B. Anemia
C. Heart failure
D. Pulmonary edema
31) The nurse assesses a client’s vision to be 20/150. The client asks for an explanation of the numbers. Which of the following would be a correct explanation for the nurse to say to the client?
A. You might need surgery to correct the nystagmus
B. You see at 20 feet what a person with normal vision sees at 150 feet.
C. You see at 150 feet what a person with normal vision sees at 20 feet.
D. You have impaired vision
32) A nurse conducting an assessment on a client’s head would do what first?
A. Inspect and palpate hair
B. Look at patient’s prior medical history
C. Inspect and palpate scalp
D. Inspect and palpate sinuses to control spread of germs
33) The nurse is planning to assess the abdomen of an adult male.
A. Place the client in side-lying position
B. Ask client to empty bladder
C. Tell client to raise arms above the head
D. Ask client to hold his breath for a few seconds
34) Normal angle at nail base is:
A. 10 degrees
B. 160 degrees
C. 180 degrees
D. 30 degrees
35) When performing an ear assessment, the nurse notes tenderness of the pinna and tragus to movement and the presence of drainage in the external canal. The nurse suspects which of the following?
A. Otitis Media
B. Otitis Externa
C. An inner ear infection
D. A negative rmberg’s sign
36) The nurse asks the client to move his eyes in the shape of an H and then in a large X. The portion of the physical assessment the nurse is completing with this client is:
A. Assessing the optic nerve
B. Assessing extra ocular muscle movements
C. Assessing the eyelids
D. Assessing the red reflex
37) As the nurse introduces the otoscope into a client’s ear, the client starts to jerk his head and complains of pain. Which of the following should the nurse do?
A. Remove the otoscope and reinsert taking care not to touch the sides of the ear canal.
B. Begin to remove the embedded cerumen.
C. Instill ear drops.
D. Document “unable to complete the examination.
38) Which cranial nerve is affected by Bell’s palsy?
A. Facial (CN VII)
B. Trigeminal (CN V)
C. Vagus (X)
D. Abducens (CN VI)
39) In medical which term is used for “impaired near vision”?
A. Amblyopia
B. Myopia
C. Presbyopia
D. Diplopia
40) During the physical examination of a male client’s scrotum, the nurse palpates a mass. What should the nurse do next with this information?
A. Perform transillumination to further assess the finding.
B. Nothing. This is a normal finding.
C. Document mass palpated, left testicle.
D. Ask the client how long he’s had a tumor in his testicle.
41) During the breast exam, the nurse asks the client to raise her arms over her head. Why did the nurse change the client’s position?
A. The client has small breasts.
B. The client has large breasts.
C. The nurse couldn’t palpate the axillae correctly.
D. Skin dimpling is accented in this position

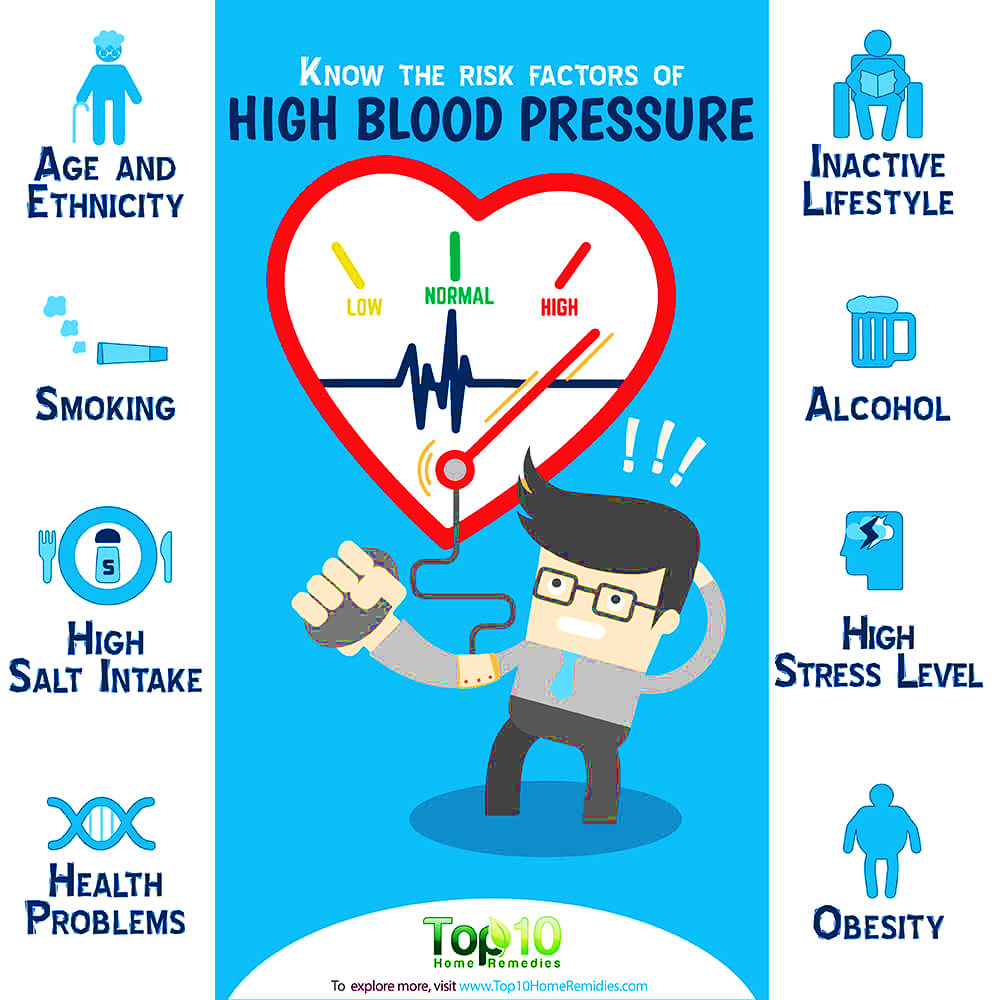 What risk factors are associated with hypertension?
What risk factors are associated with hypertension? What are common hypertension symptoms?
What are common hypertension symptoms?