Definition of Arthritis
The word “arthritis” is derived from two Greek words: arthron, meaning a joint, and – itis, meaning inflammation. Inflammation typically involves redness, heat, swelling and tenderness. So, arthritis means an inflammation joint.
Types of Arthritis
Arthritis is not a single disease with a single cause. There are dozens of different types of arthritis, each with its own cause. These are five types of arthritis which often occurs:
GOUT/GOUTY ARTHRITIS
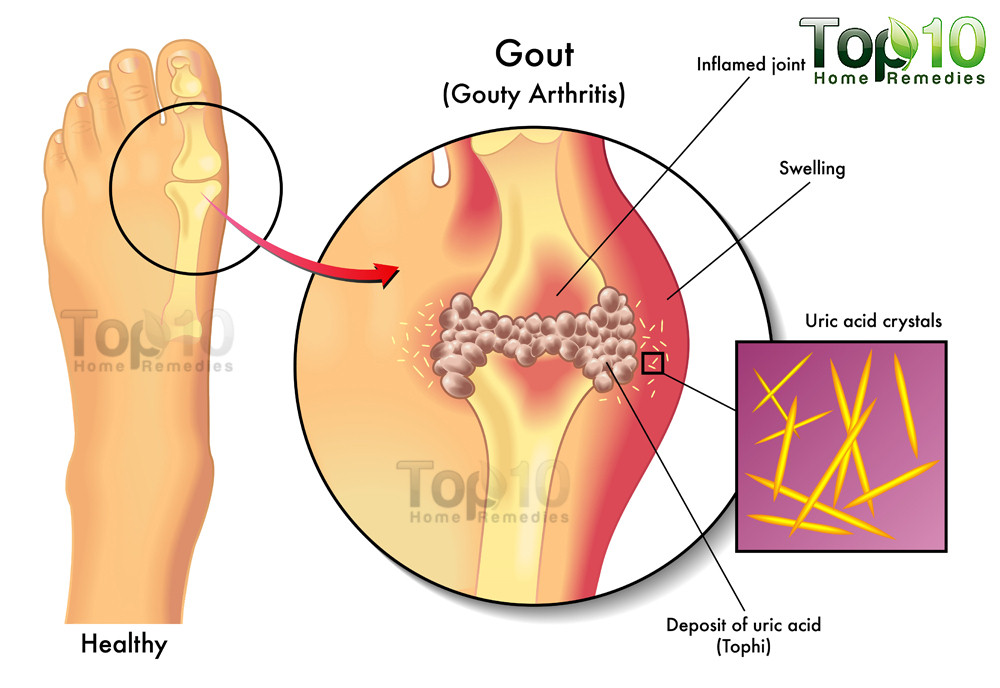
- Gout is an arthritic condition resulting from a defect in the metabolism of uric acid (hyperuricemia).
- Uric acid is the end product of purine metabolism.
- Hyperuricemia may also occur in individuals receiving chemotherapy (secondary gout).
- Deposition of urate crystals in the joint spaces.
- Build up is caused by lack of enzymes to complete purine metabolism. – Common in males.
GOUT
TOPHI
|
Also Known As
- Disease Of Kings
- ‘Disease of kings’ on the rise as more people get gout because of increase in obesity. Soaring numbers of patients are being admitted to hospital with gout triggered by obesity and heavy drinking. The painful illness is known as the disease of kings as it afflicted a number of monarchs including Henry VIII.
Incidence
- Primary gout has 85% incidence of all cases, of which 95% are men
ETIOLOGIES
- Buildup of uric acid crystals due to incomplete metabolism of purine.
- Increased production of uric acid secondary to increased cell destruction.
Pathophysiology
- In the body, uric acid is made by enzymatic breakdown of tissue and dietary purines. Huperuricemia develops because of underexcretion or overproduction of uric acid. In addition to accumulation in the blood, uric acid is concentrated in the synovial fluid, myocardium, kidneys, and ears. When uric acid levels reach a certain level, they crystallize, and the crystals (trophy) are deposited in connective tissue. Because the crystals are deposited in connective tissue, gout is classified as a form of arthritis.
CLINICAL MANIFESTATION
- Appearance of tophi.
- Arthritic joint deformities.
- Pain on the large toe on other joints.
 DIAGNOSTIC FINDING
DIAGNOSTIC FINDING
- Elevated serum uric acid.
- Joint tenderness.
- Red hot swollen joint.
- Joint fluid analysis shows characteristic of urate crystals.
NURSING INTERVENTIONS
- Assess severity and duration of pain.
- Place on bed rest; keep covers off the inflamed joint.
- Ice bag on inflamed joints.
- Avoid ASA (Aspirin) because it will increase uric acid.
- Administer prescribed medications.
- Example:
- Uricosuricagents :↑ urinal excretion of uric acids.
- Probenecid
- Sulfinpyrazone
- Allopurinol: inhibit/prevent uric acid formation.
- Monitor side effects of medications.
- Teach client and family to control gout through diet therapy.
- Increase fluid intake (prevent formation of renal stones).
PURINE CONTAINING FOOD
| A. HIGH (150-1000mg/100mg) | B. MODERATE (50-150 mg/100mg) |
| sardinesliver and kidneysweet breadmusselsmeat soupsbrain and heart | chickencrab and salmonbacon and porkbeef and hamwhole grain ricebeans and spinachasparaguscauliflower |
