- Decalcification and softening of bones.
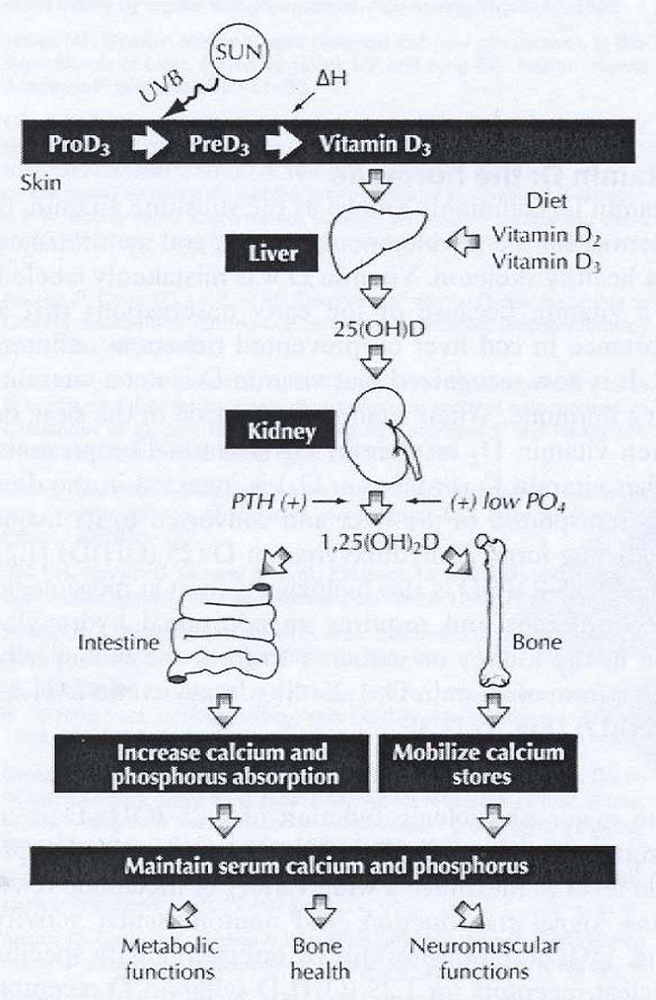
- Due to a lack of vitamin D or a problem with the body’s ability to break down and use this vitamin.
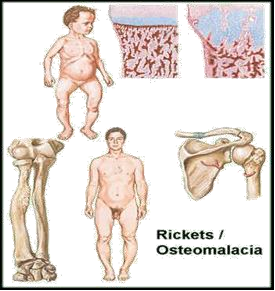
- Rickets in children.
- In adults, the condition is called osteomalacia; and in children, it’s known as rickets. Each one is a condition where prolonged and excessive vitamin D deficiency causes bones to soften, weaken, and easily fracture.
Rickets
- Disease of growing bones of children (in it epiphyseal plate not closed) in which defective mineralization occurs in both bone and cartilage of epiphyseal growth plate.
 Osteomalacia
Osteomalacia
- Disorder of mature bones in adult (after epiphyseal plate closure) in which mineralization of new osteoid bone is inadequate or delayed
RISK FACTORS
- Chronic diarrhea
- GIT malabsorption
- Lack of exposure to sunlight
- Pregnancy
- Avoidance of milk
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Renal disease
- Use of strong sunscreen
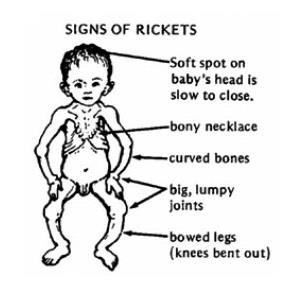
CLINICAL/DIAGNOSTIC MANIFESTATION
 Fractures
Fractures- Persistent and diffuse skeletal pain
- Progressive deformities of bones
-
- Bowed legs
- Knock knees
- Rachitic rosary
- Enlarged wrists and ankles
- Pigeon breast
-
- Progressive muscle weakness
- Decreased serum levels of Calcium (44-107 IU/L)
- Looser zones on X-ray.
- Roentgenograms shows bone demineralization and multiple bone deformities. (white: more dense; otherwise: black)
- Elevated serum alkaline phosphatase.
NURSING INTERVENTIONS
- Assess posture and gait, note ability to walk with or without aid.
- Note ability to walk requested distances.
- Check bony prominence for pressure sores.
- Assess shapes of bones throughout the body.
- Administer prescribed diet.
- Rich in Calcium
- Rich in Vitamin D (tuna, salmon, mackerel)
- Discuss purpose of physical therapy.
- Assist to a position of comfort.
- Administer prescribed analgesics.
- Gentle back massage.
- Instruct regarding home safety.
- Teach family the effects of Calcium and Vitamin D on the body and the factors affecting absorption.
- Teach client on the signs of fracture.
- Follow up care as needed.
Difference Between Osteoporosis & Osteomalacia
- Osteoporosis refers to the degeneration of already constructed bone, making them brittle,
- While osteomalacia is an abnormality in the building process of bone, making them soft.
