Research Multiple choice questions with Key
151. The use of multiple data sources to help understand a phenomenon is one strategy that is used to promote qualitative research validity. Which of the following terms describes this strategy?
a. Data matching
b. Pattern matching
c. Data triangulation
d. Data feedback
152. What is another term that refers to a confounding extraneous variable?
a. Last variable
b. First variable
c. Third variable
d. Fourth variable
153. Which of the following refers to any systematic change that occurs over time in the way in which the dependent variable is assessed?
a. Instrumentation
b. Maturation
c. Testing
d. Selection
154. Which strategy used to promote qualitative research validity uses multiple research methods to study a phenomenon?
a. Data triangulation
b. Methods triangulation
c. Theory triangulation
d. Member checking
155. In study design threats, If Subjects’ behaviour may be affected by characteristics of the researchers is known as:
a. Measurement effect
b. Experimenter effect
c. Novelty effect
d. Expectancy effect
156. Which of the following in not one of the key threats to internal validity?
a. Maturation
b. Instrumentation
c. Temporal change
d. History
157. Which is not a direct threat to the internal validity of a research design?
a. History
b. Testing
c. Sampling error
d. Differential selection
158. Internal validity refers to which of the following?
a. The ability to infer that a causal relationship exists between 2 variables
b. The extent to which study results can be generalized to and across populations of persons, settings, and times
c. The use of effective measurement instruments in the study
d. The ability to generalize the study results to individuals not included in the study
159. The post-test-only design with non-equivalent groups is likely to control for which of the following threats to internal validity:
a. History
b. Differential selection
c. additive and interactive effects
d. differential attrition
160. Which of the following designs permits a comparison of pretest scores to determine the initial equivalence of groups on the pretest before the treatment variable is introduced into the research setting.
a. One-group pretest-posttest design
b. Pretest-posttest control group design
c. Posttest-only design with nonequivalent groups
d. Both b and c
161. Which of the following control techniques available to the researcher controls for both known and unknown variables?
a. Building the extraneous variable into the design
b. Matching
c. Random assignment
d. Analysis of covariance
162. The group that does not receive the experimental treatment condition is the ________.
a. Experimental group
b. Control group
c. Treatment group
d. Independent group
163. There are a number of ways in which confounding extraneous variables can be controlled. Which control technique is considered to be the best?
a. Random assignment
b. Matching
c. Counterbalancing
d. None of the above
164. In an experimental research study, the primary goal is to isolate and identify the effect produced by the ____.
a. Dependent variable
b. Extraneous variable
c. Independent variable
d. Confounding variable
165. Which one of the following research tests hypotheses and theories in order to explain how and why a phenomenon operates as it does?
a. Descriptive
b. Predictive
c. Explanatory
d. Exploratory
166. If a research finding is statistically significant, then ____.
a. The observed result is probably not due to chance
b. The observed result cannot possibly be due to chance
c. The observed result is probably a chance result
d. The null hypothesis of “no relationship” is probably true
167. When a researcher starts with the dependent variable and moves backwards, it is called.
a. Predictive research
b. Retrospective research
c. Exploratory research
d. Descriptive research
168. Which approach is the strongest for establishing that a relationship is causal?
a. Causal-comparative
b. Correlational
c. Experimental
d. Historical
169. Following are the threats to internal validity except one;
a. Novelty Effect
b. History
c. Selection
d. Maturation
170. The degree to which the components of the research reflect the theory, concept, or variable under study is termed as;
a. Design Validity
b. Threats to Validity
c. Internal validity
d. External validity
171. Which of the following is NOT a purpose of descriptive studies?
a. To serve as a starting point for hypothesis generation
b. To get rigorous control of the variables
c. To serve as a starting point for theory development
d. To observe, describe, & document aspects of a situation as it naturally occurs
172. Which of the following attempts to understand relationships among phenomena as they naturally occur, without any intervention?
a. Ex post facto research
b. Experimental research
c. Prospective design
d. Retrospective design
173. The nursing community’s interest in qualitative research began in;
a. Late 1910’s
b. Late 1930’s
c. Late 1950’s
d. Late 1970’s
174. Which of the following is characteristic of qualitative research?
a. Generalization to the population
b. Random sampling
c. Unique case orientation
d. Standardized tests and measures
175. Which of the following is a characteristic of qualitative research?
a. Design flexibility
b. Inductive analysis
c. Context sensitivity
d. All of the above
176. Which of the following is usually not a characteristic of qualitative research?
a. Design flexibility
b. Dynamic systems
c. Naturalistic inquiry
d. Deductive design
177. Which of the following focuses on individuals’ interpretation of their experience & the ways in which they express them?
a. Historical research
b. Phenomenological Research
c. Grounded theory
d. Ethnography Research
178. Which of the following is not phase of qualitative research?
a. Orientation and overview
b. Focused exploration
c. Conformation and Closure
d. Orientation and closure
179. A research is undertaken to answer questions about causes, effects, or trends relating to past events that may shed light on present behaviors or practices is called as;
a. Historical research
b. Phenomenological Research
c. Grounded theory
d. Ethnography Research
180. Following are the major types of triangulation EXCEPT ONE;
a. Data Triangulation
b. Time Triangulation
c. Method Triangulation
d. Theory Triangulation
181. Which of the following has contributed to the development of many middle range theories of phenomena relevant to nurses?
a. Historical research
b. Phenomenological Research
c. Grounded theory
d. Ethnography Research
182. Which of the following refers to use of more than one theoretical position in interpreting data?
a. Data Triangulation
b. Time Triangulation
c. Method Triangulation
d. Theory Triangulation
183. Phenomenology has its disciplinary origins in:
a. Philosophy
b. Anthropology
c. Sociology
d. Many disciplines
184. The primary data analysis approach in ethnography is:
a. Open, axial, and selective coding
b. Holistic description and search for cultural themes
c. Cross-case analysis
d. Identifying essences of a phenomenon
185. The term used to describe suspending preconceptions and learned feelings about a phenomenon is called:
a. Axial coding
b. Design flexibility
c. Bracketing
d. Ethnography
186. ________ is a study of human consciousness and individuals’ experience of some phenomenon.
a. Phenomenology
b. Ethnography
c. Grounded theory
d. Case study research
187. ________ is a general methodology for developing theory that is based on data systematically gathered and analysed.
a. Theory confirmation
b. Grounded theory
c. Theory deduction
d. phenomenology
188. In which qualitative research approach is the primary goal to gain access to individuals’ inner worlds of experience?
a. Phenomenology
b. Ethnography
c. Grounded theory
d. Case study
189. The type of qualitative research that describes the culture of a group of people is called;
a. Phenomenology
b. Grounded theory
c. Ethnography
d. Case study
190. What term refers to the insider’s perspective?
a. Ethnocentrism
b. Emic perspective
c. Etic perspective
d. Holism
191. A researcher studies a Kashmiri group for a six month period to learn all about them so he can write a book about that particular tribe. What type of research will he likely be conducting?
a. Ethnography
b. Phenomenology
c. Grounded theory
d. Collective case study
192. _________ is used to describe cultural scenes or the cultural characteristics of a group of people.
a. Phenomenology
b. Ethnography
c. Grounded theory
d. Instrumental case study
193. Which of the following is not one of the 4 major approaches to qualitative research?
a. Ethnography
b. Phenomenology
c. Case study
d. Nonexperimental
194. Which of the following is known as a clear statement of the specific aim or goal of the study
a. Research Question
b. Research objective
c. Research Purpose
d. Research Problem
195. Tuskegee Syphilis study was conducted in which of the following year.
a. 1930
b. 1940
c. 1932
d. 1942
196. Medical experiments conduct on prisoners of war and racially valueless persons is named as;
a. Jewish C.D Hospital Study
b. Nazi medical experience.
c. Tuskegee Syphilis study
d. Willow brook Study
197. A hypothesis which states the relationship among three or more variables is called as
a. Simple Hypothesis
b. Complex Hypothesis
c. Research Hypothesis
d. Non directional Hypothesis
198. Which of the following is not an element of the ethical research?
a. Protecting subjects rights
b. Obtaining informed consent
c. Obtaining institutional approval
d. Unbalancing the benefits and the risk in the study
199. Misinforming the subjects for the research purposes is called as follow?
a. Anonymity
b. Confidentiality
c. Scientific misconduct
d. Deception
200. A hypothesis that States the nature (positive or negative) of the interaction between two or more variables is called
a. Associated Hypothesis
b. Casual Hypothesis
c. Null Hypothesis
d. Directional Hypothesis

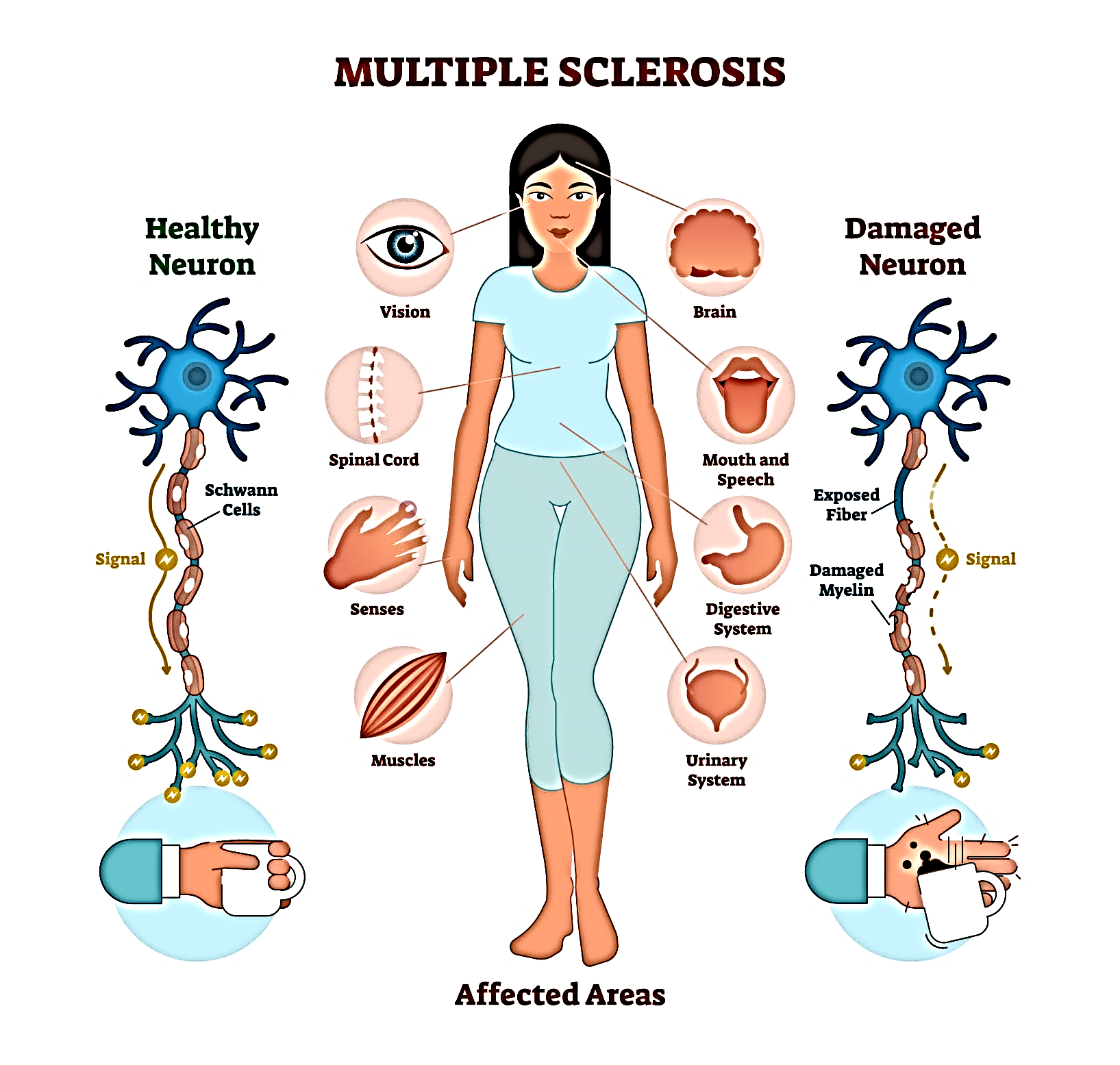 Multiple sclerosis is a disease that causes vision problems, numbness and tingling, muscle weakness, and other problems. It happens when the body’s infection-fighting system attacks and damages nerve cells and their connections in the brain and spinal cord.
Multiple sclerosis is a disease that causes vision problems, numbness and tingling, muscle weakness, and other problems. It happens when the body’s infection-fighting system attacks and damages nerve cells and their connections in the brain and spinal cord.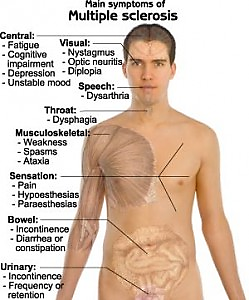 the most debilitating factor, even for those who have minimal physical restrictions, and is one of the leading causes for people leaving the workforce.
the most debilitating factor, even for those who have minimal physical restrictions, and is one of the leading causes for people leaving the workforce.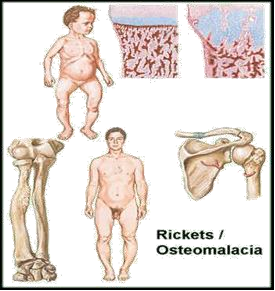 Osteomalacia
Osteomalacia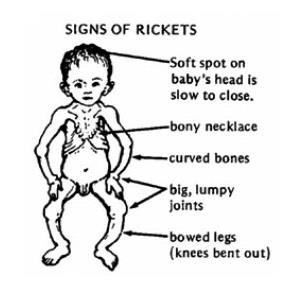 Fractures
Fractures

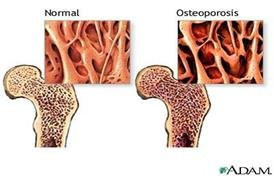
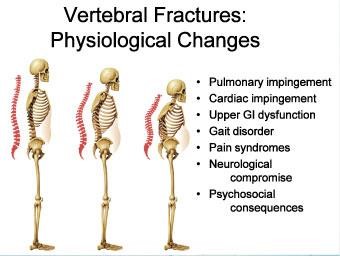 Alcohol overuse
Alcohol overuse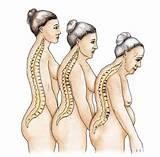
 Immobility
Immobility Provide a safe environment.
Provide a safe environment.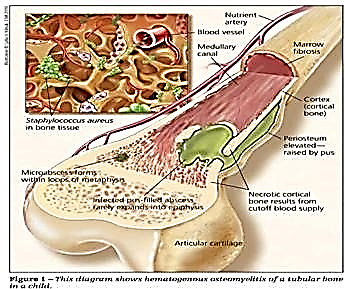 Caused by direct invasion from an open wound or a systemic infection.
Caused by direct invasion from an open wound or a systemic infection.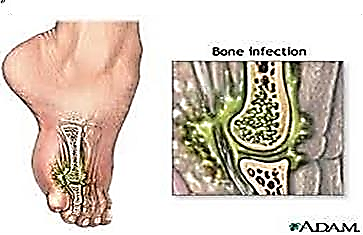
 ETIOLOGIES
ETIOLOGIES