1) It is clinical condition in which the arterial PH is greater then 7.45 PaCO3 is less then 38 mmHg.
A. Respiratory distress
B. Alkalosis & Acidosis
C. Respiratory acidosis
D. Respiratory alkalosis
2) Which nursing diagnosis is most applicable to client with fecal incontinences?
A. Risk for deficient fluid volume
B. Disturbed body image
C. Bowel incontinence
D. Altered nutrition: more than body requirement
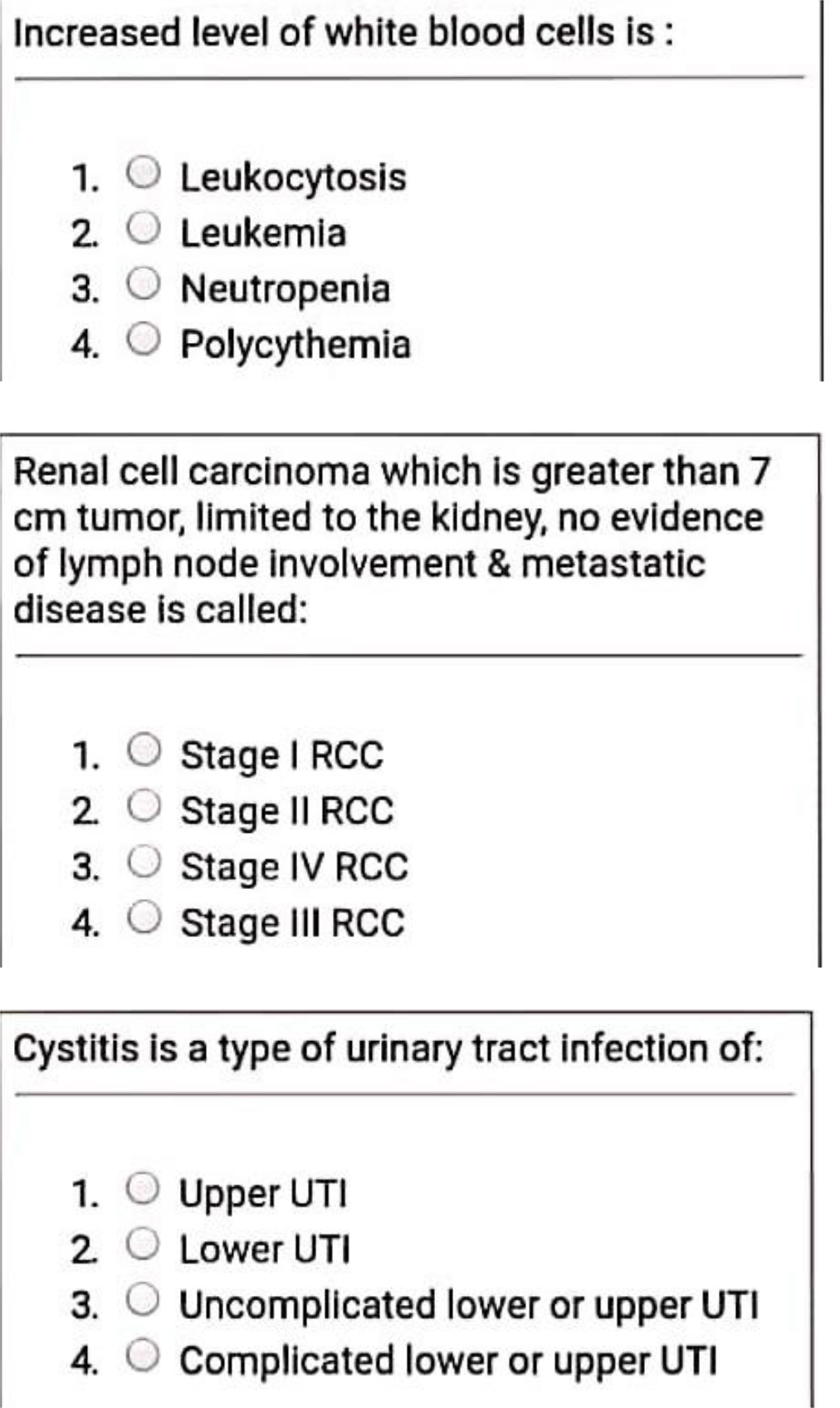
3) Cystitis is a type of urinary tract infection of:
A. Uncomplicated lower or upper UTI
B. Upper UTI
C. Complicated lower or upper UTI
D. Lower UTI
4) When counseling a client in ways to prevent cholecystitis, which of the following guidelines is most important?
A. Eat a low-fat low cholesterol diet
B. Limit exercise to 10 minutes/day
C. Keep weight proportionate to height
D. Eat a low-protein diet
5) % of abortion in the first 12 weeks of pregnancy result from chromosomal abnormalities:
A. 50 to 80
B. 20 to 30
C. 30 to 40
D. 40 to 45
6) The patient should be setting when deep breating and coughing because this position:
A. Loosens respiratory secretions
B. Helps the patient to support their incision wiht a pillow
C. Allows the patient to observe their area and relex
D. Is physically more comfortable for the patient
7) Five minutes after the client’s first post operative exercise, the client’s vital sign have not yet return to baseline. Which is an appropriate nursing diagnosis:
A. Alteration in comfort
B. Risk for activity intolerance
C. Impaired physical mobility
D. Risk for discuss syndrome
8) The doctor has ordered 500 mg of a medication po once a day. The tablets on hand are labeled as 1 tablet = 250 mg. How many tablets will you administer to your patient?
A. 03 Tablets
B. 1 Tablets
C. 02 Tablets
D. 04 Tablets
9) Foods high in purine are restricted to patients in:
A. Calcium stones
B. Oxalate stones
C. Uric acid stones
D. Struvite stones
10) What is/are the most common cause(s) of chronic liver disease?
A. Obesity
B. Bacteria
C. Gall bladder stones
D. Alcohol abuse
11) Inflammation of the lower end of the esophagus leading to a back flow of gastric juices is called:
A. Structural abnormalities
B. Lactose intolerance
C. Acid reflux
D. Reflux esophagitis
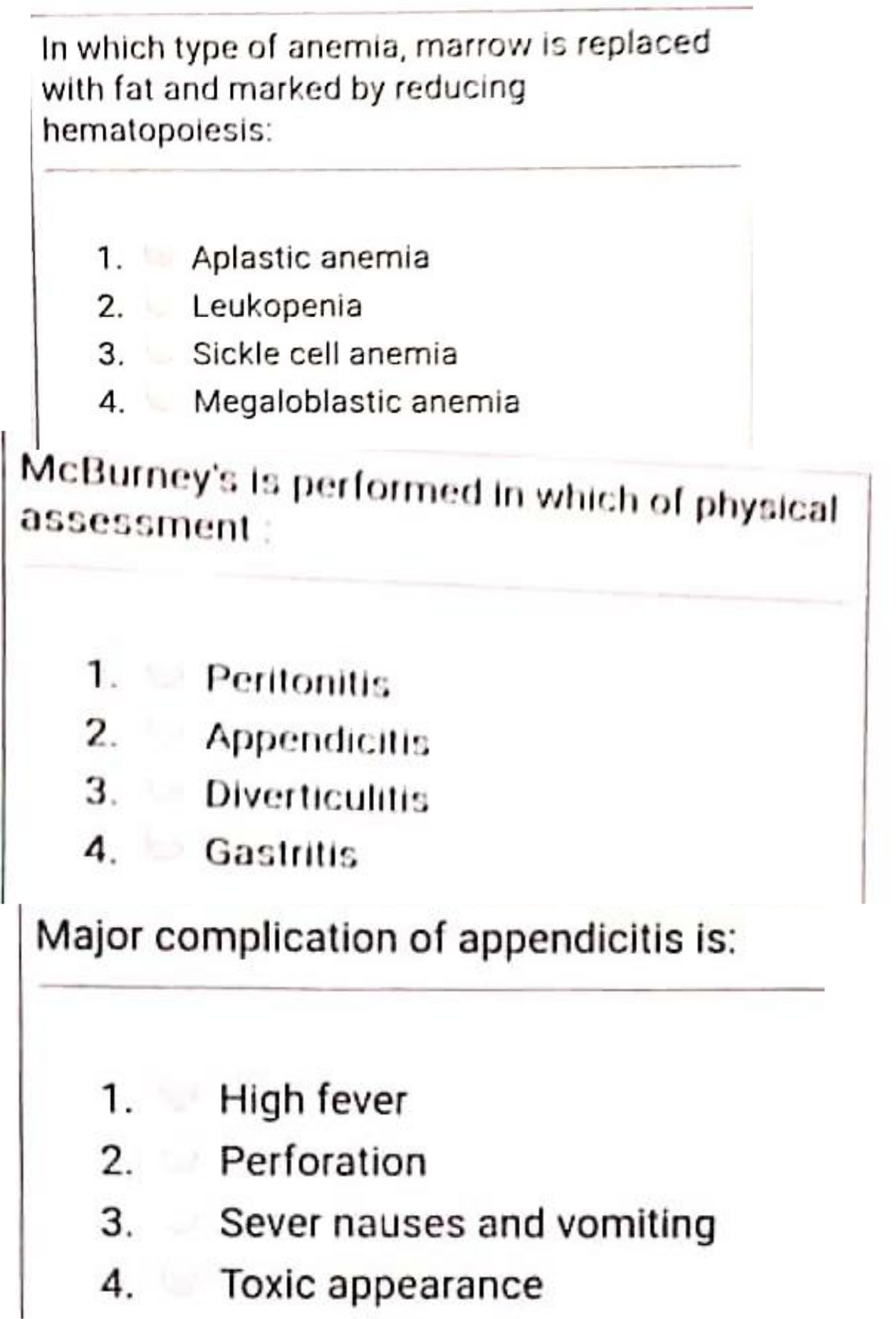
12) Which statement about appendicitis is accurate and true?
A. Mc Burney’s point tenderness is suggestive of appendicitis
B. Lefty lower quadrant pain is suggestive of a appendicitis
C. Appendicitis is more common among females than males
D. A high fiber diet is a risk factor associated with appendicitis
13) Renal cell carcinoma which is greater than 7 cm tumor limited to the kidney, no evidence of lymph node involvement & metastatic disease is called:
A. Stage II RCC
B. Stage I RCC
C. Stage IV RCC
D. Stage III RCC
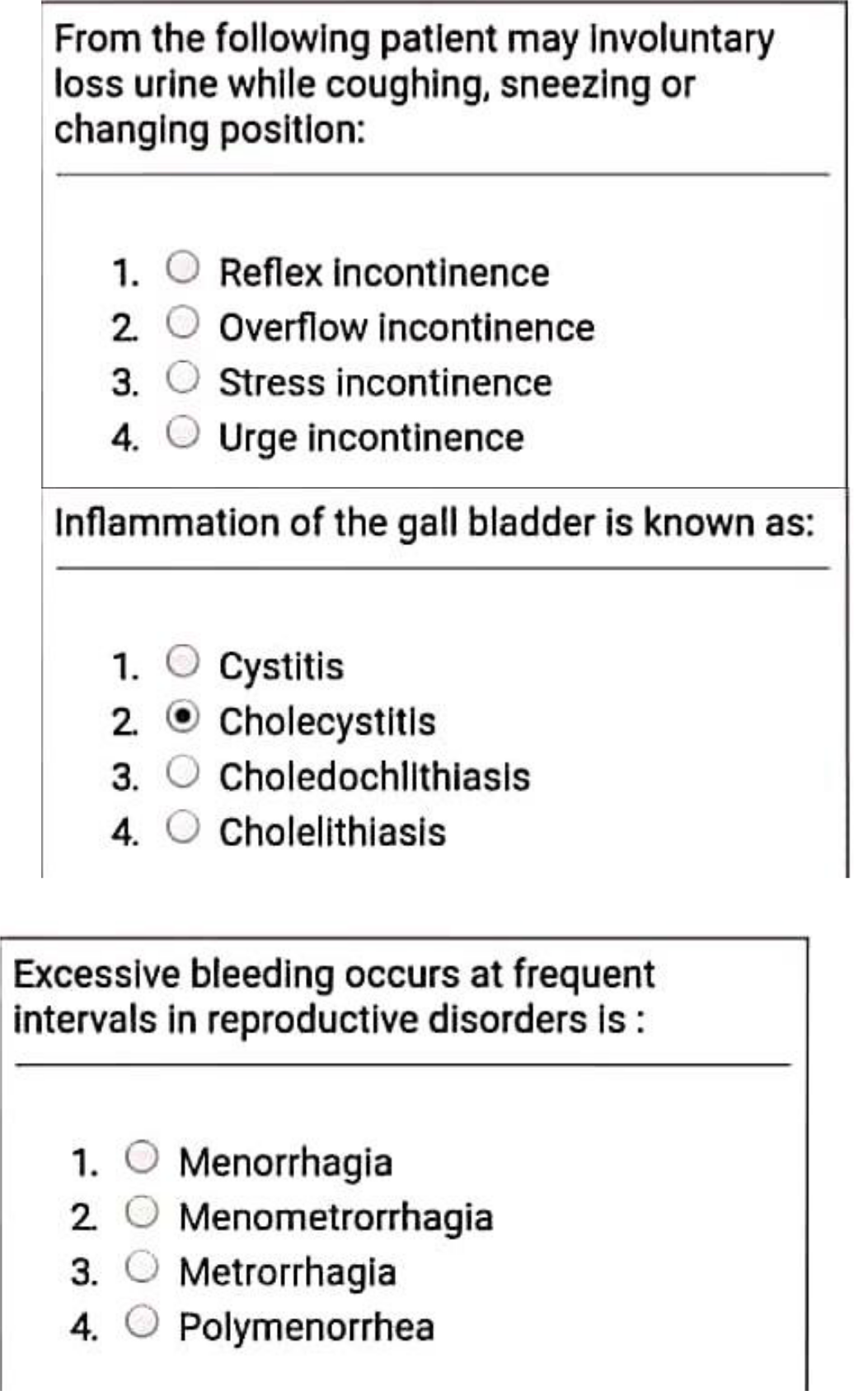
14) Excessive bleeding occurs at frequent intervals in reproductive disorders is:
A. Menometrorrhagia
B. Menorrhagia
C. Polymenorrhea
D. Metrorrhagia
15) A hernia is the of an organ or tissue out of the body cavity in which it is normally found:
A. Trauma
B. Syndrome
C. Protrusion
D. Pressure
16) Swelling of the salivary glands in mumps is called:
A. Periodontitis
B. Parotitis
C. Granuloma
D. Salivitis
17) Painless enlargement of one or more lymph nodes on one side of the neck is:
A. Tuberculosis
B. Non Hodgkin disease
C. Lymphomas
D. Hodgkin’s Disease
18) When establishing realistic goal, the nurse:
A. Bases of the goals on the narse’s personal knowledge
B. Must have the client cooperation
C. Knows the resourses of the health care facility, family and the client
D. Must have a client who is phyiscally and emotionally stable
19) Puberty age in female is:
A. 18 to 19 years
B. 19 to 20 years
C. 16 to 17 years
D. 10 to 14 years
20) A client being treated for chronic cholecystitis should be given which of the following instructions?
A. Use anti cholinergic as prescribed
B. Increase protein in diet
C. Avoid antacids
D. Increase rest
21) Which nursing diagnosis is most applicable to client with fecal incontinence?
A. Altered Nutrition:more than body requirement
B. Risk for Deficient fluid volume
C. Bowel Incontinence
D. Disturbed body image
22) What can reduce a patient’s anxiety and postsurgical pain?
A. Preoperative checklist
B. Psychological counseling
C. Preoperative teaching
D. Preoperative medication
23) A hiatus hernia occurs when the upper part of the stomach is dislocated through the hole, called a Hiatus, in the , into the chest:
A. Duodenum
B. Abdominal cavity
C. Diaphragm
D. Esophagus
24) Mechanical obstruction of intestine in which bowel twists and turns on itself:
A. Adhesions
B. Amyloidosis
C. Volvulus
D. Stenosis
25) Which electrolyte is essential for enyzme and neurological activities?
A. Magnesium
B. Phosphate
C. Potassium
D. Chloride
26) Which of the following stage the carcinogen is irreversible?
A. Progression stage
B. Promotion stage
C. Initiation
D. Regression
27) From the following nursing diagnosis which is suitable for hemorrhoids:
A. Urinary retention related to postoperative reflux spasm and fear of pain
B. Imbalance nutrition less than body requirement
C. Anxity related to surgical intervention
D. Constipation related to ignoring the urge to defecate because of pain during elimination
28) Which one is the best investigation to find out the stone in urinary tract:
A. Ultrasound
B. M.R.I
C. I.V.P
D. CT scan
29) Which is the most common complication of peptic ulcer disease?
A. Haemorrhage
B. Penetration
C. Gastric outlet obstruction
D. Perforation
30) In what order should one perform an abdominal assessment:
A. Inspection, percussion, palpitation, auscultation
B. Inspection, auscultation, percussion, palpitation
C. Percussion, Palpitation, Inspection, Auscultation
D. Palpitation, Inspection, Percussion,. auscultation
31) From the following in which operation patient needs sitz bath:
A. Appendectomy
B. Colostomy
C. Hysterectomy
D. Hemorrhoids
32) Food poisoning “should be suspected with persons who shared food within the previous 1-6 hours, and symptoms of nausea, vomiting,and idarrhea, typically, this is due to:
A. Emetics
B. Infection
C. Intoxication
D. Inebrition
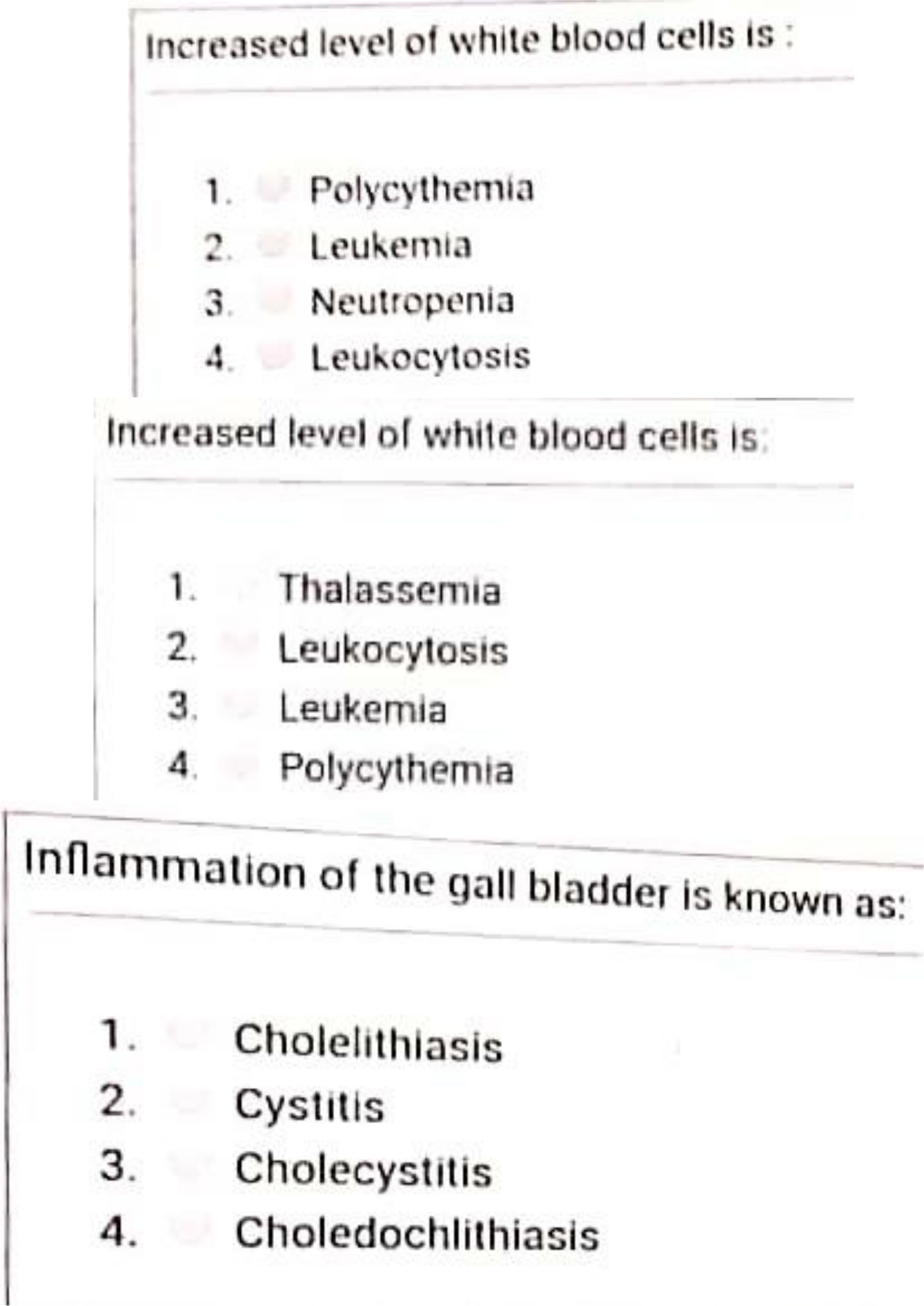
33) Is a malignant disorder of hemopoietic tissues, associated increased number of
leukocytosis in the blood:
A. Hemophilia
B. H. Influenza
C. Leukemia
D. Poly cythemia
34) is primarily a disease of children older than 2 years of age:
A. Acute glomerulonephritis
B. Nephrotic syndrome
C. Renal abscess
D. Acute pyelonephritis
35) Spread of cancer cells from the primary tumor to distant sites:
A. Dysplasia
B. Metaplasia
C. Malignant
D. Metastasis
36) What intervention is the best relieve constipation during pregnancy?
A. Lying flat on back when sleeping
B. Taking a mild over-the counter laxative
C. Reduction of iron intake by half or more
D. Increasing the consumption of fruits and vegetable
37) Anemia which can be classified based on the body temperature and antibodies react with the RBC antigen is:
A. Polycythemia
B. Aplastic anemia
C. Immune hemolytic anemia
D. Hemolytic anemia
38) is disorder in which bone lose density and become porous and fragile:
A. Menarche
B. Osteoporoses
C. Formix
D. Dysmenoria
39) The most appropriate tool in confirmation of malignancy in the patient is:
A. History
B. Physical examination
C. Blood CP
D. Biopsy of tissue
40) Normal Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) per minute is:
A. 115 ml
B. 100 ml
C. 105 ml
D. 120 ml