Islamiat |1stYear| 2nd Semester| BSN (Generic)
- The conquest of Makkah was held in year:
A) 6 hijra
B) 9 hijra
C) 7 hijra
D) 8 hijra
E) 10 hijra - The name of grandfather of the Holy Prophet (P.B.U.H):
Abdul Mutalib
3. The Qureshi were used profession of
A) Farming
B) Teaching
C) Trading
D) Hunting
E) Fishing
4. When Prophet Muhammad(PBUH) left his followers physically the Muslims take an oath on the hand of:
A) Hazrat Ali R.A
B) Hazrat Abu Bakar R.A
C) Hazrat Usman R.A
D) Hazrat Talha R.A
E) Hazrat Umar R.A
5. The batle of Khyber was fought in hijrah:
A) 9th
B) 7th
C) 5th
D) 8th
E) 6th
6. The First Battle was fought between Muslim of Madina Quraish of Makkah was:
A) Khyber
B) Muta
C) Khandak
D) Uhad
E) Badar
7. In the battle of Baddr the leader of Quraysh was :
A) Aamir Al Hazar
B) Utbabin Rabia
C) Abu Sufyan
D) Abu Jihil
E) Umar bin abdwud
8. The name of the 1st wife of the Prophet (P.B.U.H):
A) Bibi Ume-e-Salma R.A
B) Bibi Ayesha R.A
C) Bibi Hafsa R.A
D) Bibi Khadija R.A
E) Bibi Safia R.A
9. Hazrat Ali R.A belong to:
A) Bano Quraiza
B) Bano Nazir
C) Bano Hashim
D) Bano Abbas
E) Bano Ummya
10. The Name of The Prophet whom the people had took into the fire was:
A) Hazra Essa A.S
B) Hazrat Zakarya A.S
C) Hazrat Ibrahim A.S
D) Hazrat Mussa A.S
E) Hazrat Daud A.S
11. The number of Khulafa-e-Rashdin are:
A) Two
B) Five
C) Three
D) Four
E) Six
12. The prophet (P.B.U.H) go this 1st marriage at the age of:
A) 25 years
B) 35 years
C) 30 years
D) 20 years
E) 40 years
13. In Battle of Uhud the number of Muslim Army was:
A) 600
B) 900
C) 700
D) 1000
E) 800
14. Abu Jahl Was Killed In battle of:
A) Khandak
B) Badar
C) Khyber
D) Hunain
E) Uhad
15. In The Islamic History the 1st time“Azan”call for prayer was given by:
A) Hazrat Usman
B) Hazrat Ali
C) Hazrat Umar
D) Hazrat Bilal
E) Hazrat Zubair
16. The work of taken out soul from the human body is done by the angel:
A) Hazrat Izraeel A.S
B) None of these
C) Hazrat Meekail A.S
D) Hazrat Israfeel A.S
E) Hazrat Jibraeel A.S
17. When the Holy Prophet Muhammad (PBUH) left for Madinah from Makkah, he stays on his bed:
A) Hazrat Usman R.A
B) Hazrat Ali R.A
C) Hazrat AbuBakar R.A
D) Hazrat Umar R.A
E) Hazrat Hassan R.A
18. Khana Kabah was built by:
A) Hazrat Moosa A.S
B) Hazrat Mutalib
C) Hazrat AbuTalib
D) Hazrat Daud A.S
E) Hazrat Ibrahim A.S
19. The Name of the1st daughter of the Holy Prophet (P.B.U.H):
A) Bibi Ruquia R.A
B) Bibi Sakeena R.A
C) Bibi Zainab R.A
D) Bibi Ume Kulsoom R.A
E) Bibi Fatima R.A
20. The Holy book “Quran” was revealed on the prophet:
A) Hazrat Muhammad (PBUH)
B) Hazrat Zakria A.S
C) Hazrat Daud A.S
D) Hazrat Essa A.S
E) Hazrat Mussa A.S
21. The pact of Messak-e-Madina was held in:
A) 1st Hijrah
B) 4th Hijrah
C) 2nd Hijrah
D) 3rd Hijrah
E) 5th Hijrah
22. The Heart of Holy Quran is:
A) Suray Taha
B) Surah Al Ahzab
C) Surah Furqan
D) Surah Yaseen
E) Surah Rehman
23. The total no. of the Holy verses of the “Quran” are:
A) 113
B) 116
C) 114
D) 117
E) 115
24. The saying of the Holy Prophet Muhammad(PBUH)is known as:
A) Sahifa
B) Fiqah
C) Quran
D) None of these
E) Hadees
25. The sacred building of Islam is situated in the center of Makkah is known as:
A) Arafat
B) Kabah
C) Meekat
D) Riazul Janat
E) Janatul Baqi
26. The Prophet (P.B.U.H) tookhis1st travel with his mother in the age of:
A) 8 years
B) 9 years
C) 7 years
D) 6 years
E) 5 years
27. The last pillar of Islam is:
A) Nimaz
B) Fasting
C) Zakat
D) Haj
E) Kalma Tayaba
28. The Number of Devine books are:
A) Three
B) One
C) Two
D) Five
E) Four
29. The wife of Holy Prophet Muhammad (PBUH) Bibi Ayesha R.A was the daughter of:
A) Hazrat Umar R.A
B) Hazrat Zaid R.A
C) Hazrat Abu Bakar R.A
D) Hazrat Usman R.A
E) Hazrat Zubair R.A
30. The longest surah of the Holy Quran is:
A) Surah Alaq
B) Surah Al Hijrat
C) Surah Yaseen
D) Surah Rehman
E) Surah Baqarah
31. The revelation of the holy Quran was through the angle:
A) Meekaile A.S
B) Izraiel A.S
C) Israfeel A.S
D) Jibraiel A.S
E) None of these
32. The fasting has been done in the month of:
A) Safar
B) Shouban
C) Rajab
D) Moharam
E) Ramzan
33. When Bibi Khadija Got The marriage with the Prophet (P.B.U.H) her age was:
A) 25 years
B) 40 years
C) 30 years
D) 45 years
E) 35 years
34. Due to the social boycott of Quraish of Makkah the family of Hazrat Abu Talif has stay in the valley “Shoaib Abi Talib” almost:
A) Four year
B) One year
C) Three year
D) Five year
E) Two year
35. The Holy Prophet (P.B.U.H) delivered his last sermon at the place of:
A) Taif
B) Uhad
C) Arafat
D) Hudabia
E) Safa Marvah
36. Batle of Uhad was fought in the year of :
A) 5 hijri
B) 6 hijri
C) 4 hijri
D) 3 hijri
E) 2 hijri
37. The Prophet (P.B.U.H) belongs to the linage of:
A) Hazrat Daud (A.S)
B) Hazrat Noonh (A.S)
C) Hazrat Ibrahim (A.S)
D) Hazra tMussa (A.S)
E) Hazrat Idrees (A.S)
38. 1st Soorah of the Holy Quran:
A) Surah Alaq
B) Surah Fateh
C) Surah Ikhlas
D) Surah Naas
E) Surah Falaq
39. The Prophet (P.B.U.H) had preached Islam hiddenly almost :
A) 2 year
B) 5 year
C) 1 year
D) 3 year
E) 4 year
40. Bait-e-Uqba Oola has been in the year of Nabvi:
A) 13
B) 14
C) 11
D) 12
E) 10
Answer key:
1. D
2. Abdul Mutalib
3. D
4. B
5. B
6. D
7. D
8. D
9. D
10. C
11. D
12. A
13. D
14. B
15. D
16. A
17. B
18. E
19. C
20. A
21. A
22. D
23. A
24. E
25. B
26. E
27. D
28. E
29. C
30. E
31. D
32. E
33. B
34. C
35. C
36. D
37. C
38. B
39. D
40. E

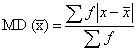
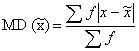
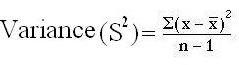 Formula
OR S2 =
Calculating variance: Heart rate of certain patient is 80, 84, 80, 72, 76, 88, 84, 80, 78, & 78. Calculate variance for this data.
Solution:
Step 1:
Find mean of this data
Formula
OR S2 =
Calculating variance: Heart rate of certain patient is 80, 84, 80, 72, 76, 88, 84, 80, 78, & 78. Calculate variance for this data.
Solution:
Step 1:
Find mean of this data
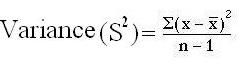 Variance = 184/ 10-1 = 184/9
Variance = 20.44
Standard Deviation
Variance = 184/ 10-1 = 184/9
Variance = 20.44
Standard Deviation
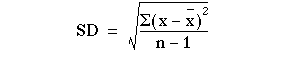 Formula:
OR S =
Calculating Standard Deviation (we use same example): Heart rate of certain patient is 80, 84, 80, 72, 76, 88, 84, 80, 78, & 78. Calculate standard deviation for this data.
SOLUTION:
Step 1: Find mean of this data
Formula:
OR S =
Calculating Standard Deviation (we use same example): Heart rate of certain patient is 80, 84, 80, 72, 76, 88, 84, 80, 78, & 78. Calculate standard deviation for this data.
SOLUTION:
Step 1: Find mean of this data
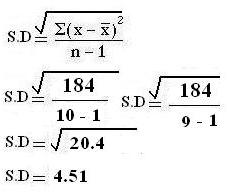 MERITS AND DEMERITS OF STD. DEVIATION
MERITS AND DEMERITS OF STD. DEVIATION
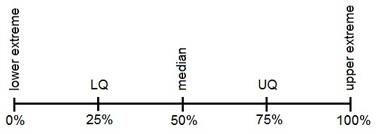
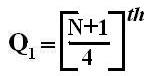
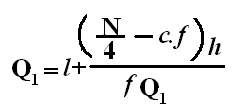
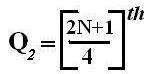
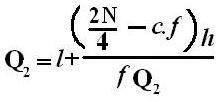
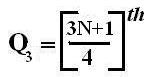
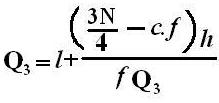
 Symbol Key:
Symbol Key:
