Fundamental of Nursing MCQs/BCQs BSc Nursing
1. A walk-in client enters into the clinic with a chief complaint of abdominal pain and diarrhea. The nurse administered anti diarrheal tablets to the patient. What phrase of nursing process is being implemented here by the nurse?
A. Assessment
B. Diagnosis
C. Planning
D. Implementation
2. It is best describe as a systematic, rational method of planning and providing nursing care for individual, families, group and community.
A. Assessment
B. Nursing Process
C. Diagnosis
D. Implementation
3. The 1st technique used in examining the abdomen of a client is:
A. Palpation
B. Auscultation
C. Percussion
D. Inspection
4. During a routine examination you are assessing the putting pressure on the patient’s abdomen to evaluate that whether the patient is having tenderness or not, you are performing which of the following technique:
A. Palpation
B. Auscultation
C. Inspection
D. Percussion
5. The nurse is using otoscope for assessing the patient. Which of the following area is tested?
A. Optic
B. Olfactory
C. Oculomotor
D. Trochlear
6. A nurse is performing an initial assessment for a client. Which of the following could be considered objective information except?
A. The client’s blood pressure increases when the provider enters the room
B. The client weighs 186 pounds
C. The client rates pain at a level of 6 on the numeric rating scale
D. The client has a pinpoint rash on the face and trunk
7. A patient comes to the health care setup, you are assessing the patient and you gathered information about the patient current health status and past health status, you are doing..
A. Assessment
B. Interviewing
C. Data Collection
D. All of the above
8. A patient is brought to ED in unconscious status, you gathered data from the patient’s relatives or attendants, this type of data can be labeled as_________________
A. Primary source of data
B. Objective data
C. Secondary source of data
D. All of the above
9. During your conversation for gathering data, you asked several questions from the patient and you got the answers for those questions, you are using ________________ skill for data collection.
A. Objective data
B. Secondary data
C. Source of data
D. None of the above
10. The component of the nursing diagnose that shows the client’s health status and directs the nurse towards the formation of the nursing interventions is___________________
A. Etiology
B. Defining characteristics
C. Problem Statement
D. None of the above
11. The Nurse is providing physical care, emotional support, comfort, teaching, counseling and environmental support to the patient, all these interventions can be labeled as _______________
A. Dependent interventions
B. Independent interventions
C. Collaborative interventions
D. Systematic interventions.
12. Nursing documentation can be use in the following aspects:
A. Communication
B. Education
C. Both A & B
D. None of the above
13. While preparing the patient for surgery, Nurse is taking signatures from the patient or the patient’s relative to allow for the surgery, this document is called_______________
A. Medical record
B. Detailed chart
C. Check list
D. Patient assessment form
E. None of the above
14. The organized, purposeful and disciplined thinking process is known as______________
A. Deep thinking
B. Enhanced thinking
C. Critical thinking
D. Dependent thinking
15. The following are the steps that are involved in critical thinking_____________
A. Interpretation
B. Analysis
C. Evaluation
D. Self regulation
E. Both A & B
F. All of the above
16. An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage is known as:
A. Pain
B. Stimulus
C. Stress
D. None of the above
17. A 50 year old male patient is admitted in the medicine department, is complaining of the pain in the right lower limb, The nurse assessed the patient and was unable to know the etiology of the pain, this pain can be labeled as ________________
A. Nociceptive pain
B. Psychogenic pain
C. Neuropathic pain
D. Relative pain.
18. A 62 year old patient is brought to the Emergency Department, with severe chest pain on the left side, spreading towards the left shoulder and left arm, when the nurse assessed the patient she came to know that the patient is suspected for MI, the nurse labeled the type of pain as_____
A. Phantom pain
B. Referred pain
C. Radiating pain
D. Psychogenic pain
19. Retrosternal chest pain can be labeled as______________
A. Phantom pain
B. Referred pain
C. Radiating pain
D. Psychogenic pain
20. A 780 year old patient is brought to the Emergency Department, with diabetic foot gangrene with severe pain in the foot, the doctor performed surgery and amputated the foot, post operatively the patient was perceiving pain in the foot, the nurse informed the doctor that the patient is having _________________ pain.
A. Referred pain
B. Radiating pain
C. Psychogenic pain
D. Nociceptive pain
E. None of the above
21. According to this theory pain is produced when any sensory nerve is stimulated to a certain level:
A. Intensity theory
B. Specificity Theory
C. Gate control Theory
D. All of the above
22. All of the following are Non Pharmacological measures for relieving pain except__________
A. Distraction
B. Humor
C. Music
D. Opoids
E. Relaxation
23. The sum of all the interactions between an organism and the food it consumes is called_____
A. Nutrients
B. Nutrition
C. Food availability
D. All of the above
24. Rate at which food is metabolized to maintain energy requirements of a person who is awake and at rest
A. Catabolism
B. Anabolism
C. Basal Metabolic Rate
D. Metabolism
25. The nurse is assessing a 3 year old baby for nutritional status, The nurse measures the Height and weight, Growth curve, Head and chest circumferences, Skin fold thickness, and Mid arm circumference, the nurse asks the student nurse that which type of measurements she had taken, the student nurse will answer _______________
A. Anthropometric measurement
B. Body measurement
C. Height and weight
D. Physical measurement
26. You are asked to calculate the BMI for the patient having Weight = 70 kg (154 lb) and Height= 5 feet (60 inches or 1.52 m) , what will be the BMI of the patient _____________
A. 20
B. 30.1
C. 55
D. 22
27. You calculated the BMI of the patient in question no. 26, look at the patient BMI and label the patient into one category:
A. Under weight
B. Normal weight
C. Obesity
D. None of the above
28. You are taking history from the patient at OPD, and the patient tell you that he pass feces 2 times a day in routine, he tells now he has not passed stool from 4 days, the nurse will consider that the patient is having:
A. Diarrhea
B. Constipation
C. Flatulence
D. Bowel incontinence
29. If constipation is prolonged it can lead to _____________
A. More Constipation
B. Bowel incontinence
C. Fecal impaction
D. Fecal incontinence.
30. A 25year old male patient is admitted in the medicine department, is complaining of excessively liquid stool, Difficult to control urge for defecation and Spasmodic cramps, on assessment you came to know that the patient is dehydrated and have increase bowel sound, what will be your diagnoses?
A. Diarrhea
B. Constipation
C. Flatulence
D. Bowel incontinence
31. The loss of voluntary ability to control the fecal and gaseous discharge through the anal sphincter is called _________________
A. Diarrhea
B. Constipation
C. Flatulence
D. Bowel incontinence
32. you are taking history from the patient, and the patient tells you that he is unable to control flatus, as well as complain of minor soiling: you can consider this condition as___________
A. Diarrhea
B. Partial bowel incontinence
C. Major bowel incontinence
D. None of the above.
33. The presence of excessive flatus in the intestines is called_______________
A. Diarrhea
B. Constipation
C. All of the above
D. None of the above
34. A nursing student ask you a question that, in which stage of sleep the dreaming occurs, what will be your answer ????
A. NREM Stage 3
B. NREM Stage 4
C. REM Stage
D. Deep Sleep Stage
E. All of the above
35. While caring for a client with disturbed sleep pattern, which of the following will be your nursing intervention on priority?
A. Maintain a good circadian rhythm
B. Get adequate exercise during day time, but avoid excessive exertion before bed time.
C. Avoid dealing with office work or family problem before bedtime.
D. Use the bed mainly for sleep, so that you associate it with sleep.
36. The most common form of sexual activity is _______________
A. Homosexual genital intercourse
B. Orgasm
C. Libido
D. Heterosexual genital intercourse
37. Sexual response cycle includes the following phases except__________
A. Excitement phase
B. Plateau phase
C. Maintenance phase
D. Orgasmic phase
E. Resolution phase
38. “Many sexual therapist advise to increase sexual communication to avoid this problem” which of the following best justifies the above statement.
A. Erectile dysfunction
B. Pre mature Ejaculation
C. Dysparunia
D. All of the above
39. The chronic vulvar discomfort or pain that characterized by complaints of burning or pain or irritation of the female genitalia is known as:
A. Dysparunia
B. Vaginal infection
C. Vulvodynia
D. Vaginismus
40. You are on duty in urology department and you are asked to, asses the male patient’s genital organs, you will assess all of the following in physical examination except?
A. Inspect for any scars or lesions on the external genitals.
B. Ask for Current problem in sexual activity
C. Inspect for any changes in the shape of genital organs.
D. Compare the size of both testes
41. Nurse Elisabeth is teaching about sexual health to client, she taught about various things, some of them are the following, the head nurse noted Elisabeth that all of her teaching was right except:
A. Encourage open communication between partners.
B. Teach about kegel exercise to women.
C. Teach about any changes in sexual pattern due to any medications or following surgical procedure.
D. Do you have any problem in your sexuality?
42. The permanent cessation of function of vital organs of the body, including heart beat, spontaneous breathing and brain activity is known as_____________
A. Rest
B. Sleep
C. Death
D. All of the above
43. You have a 75 years old patient in ICU in critical condition, the physician tells you that the patient is not in satisfactory condition and going towards death, he noted the following manifestation and made his statement:
A. Loss of muscle tone
B. Slowing of the circulation
C. Changes in the vital signs
D. Sensory impairment
E. All of the above
F. None of the above
44. In the same case (as in question 43), the patient is expired, and the doctor declares the patient death, on which of the following basis the doctor declared this death?
A. Total lack of response to external stimuli
B. No muscular movement
C. No reflexes
D. Flat encephalogram
E. All of the above
F. Both B, C and D
45.” Does not understand concept of death, believes death is reversible, temporary departure or sleep.” From whom we can expect the above mentioned response?
A. A 5 year child
B. An Adult
C. A person in late adulthood
D. None of the above
46. “Fears prolonged illness, sees death as having multiple meanings, freedom from pain, and reunion with already deceased family members” From whom we can expect the above mentioned response?
A. An Adult having age of 20 years
B. A child
C. Above 65 years
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
47. The stiffening of the body that occurs about 2 to 4 hours after death is called _____________
A. Algor Mortis
B. Rigor Mortis
C. Livor Mortis
D. Stiffening of the body
E. Discoloration
48. _______________Is the gradual decrease of the body temperature after death.
A. Algor Mortis
B. Rigor Mortis
C. All of the above
D. None of the above
49. The loss that can be identified by others and can arise in response to a situation is called_________
A. Anticipatory loss
B. Perceived loss
C. Actual loss
D. None of the above
50. All of the following are Kubler Ross propose stages of grief except____________
A. Denial
B. Adopting
C. Anger
D. Depression.

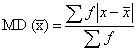
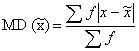
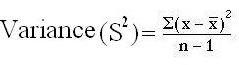 Formula
OR S2 =
Calculating variance: Heart rate of certain patient is 80, 84, 80, 72, 76, 88, 84, 80, 78, & 78. Calculate variance for this data.
Solution:
Step 1:
Find mean of this data
Formula
OR S2 =
Calculating variance: Heart rate of certain patient is 80, 84, 80, 72, 76, 88, 84, 80, 78, & 78. Calculate variance for this data.
Solution:
Step 1:
Find mean of this data
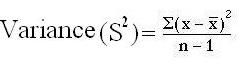 Variance = 184/ 10-1 = 184/9
Variance = 20.44
Standard Deviation
Variance = 184/ 10-1 = 184/9
Variance = 20.44
Standard Deviation
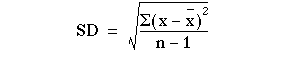 Formula:
OR S =
Calculating Standard Deviation (we use same example): Heart rate of certain patient is 80, 84, 80, 72, 76, 88, 84, 80, 78, & 78. Calculate standard deviation for this data.
SOLUTION:
Step 1: Find mean of this data
Formula:
OR S =
Calculating Standard Deviation (we use same example): Heart rate of certain patient is 80, 84, 80, 72, 76, 88, 84, 80, 78, & 78. Calculate standard deviation for this data.
SOLUTION:
Step 1: Find mean of this data
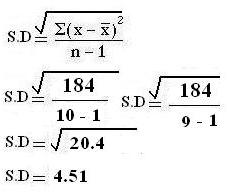 MERITS AND DEMERITS OF STD. DEVIATION
MERITS AND DEMERITS OF STD. DEVIATION
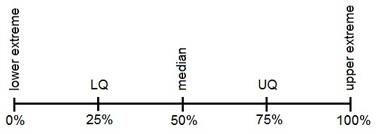
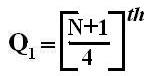
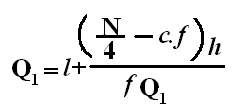
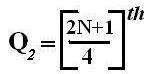
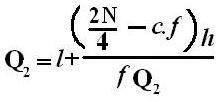
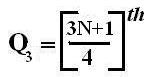
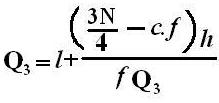
 Symbol Key:
Symbol Key:
