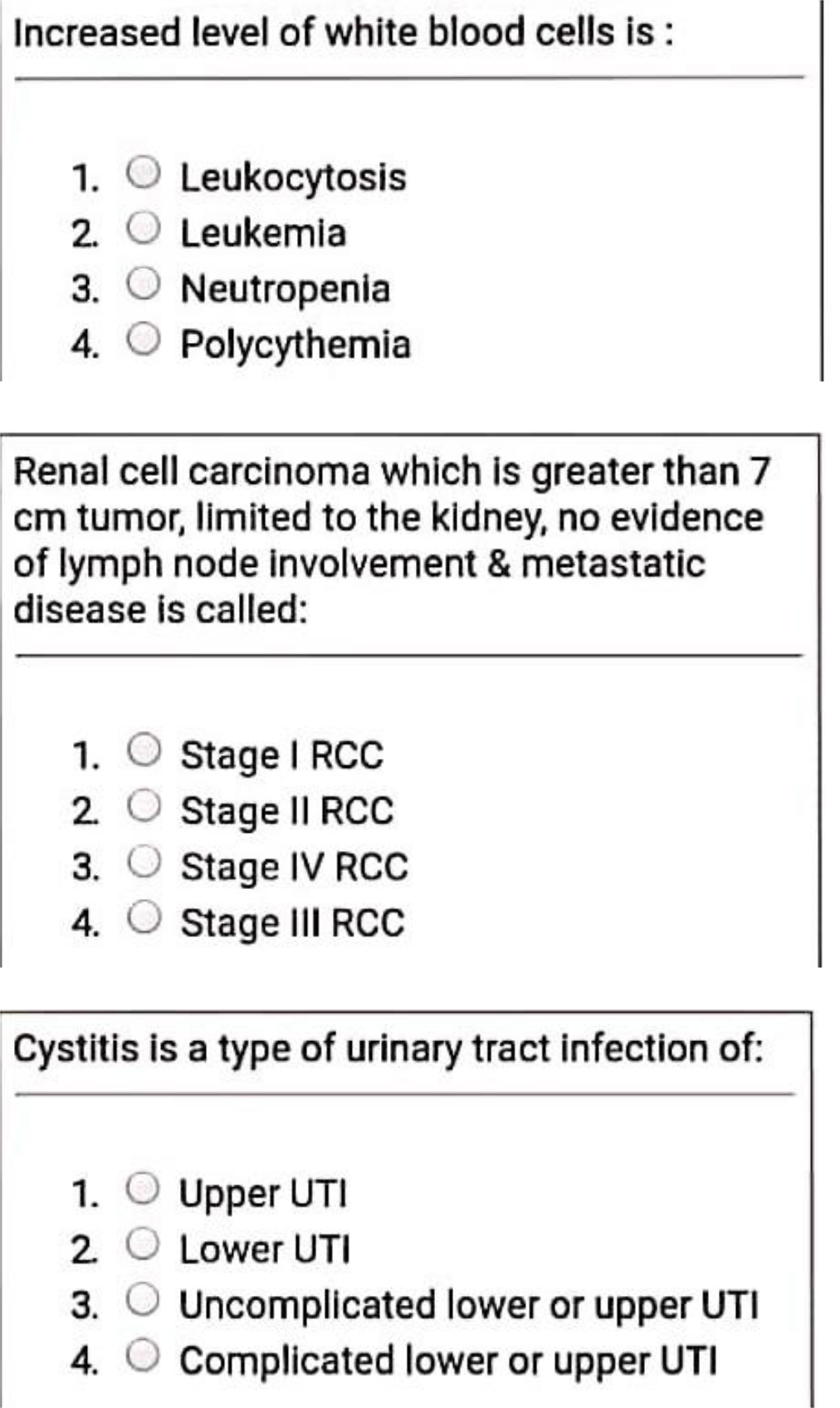
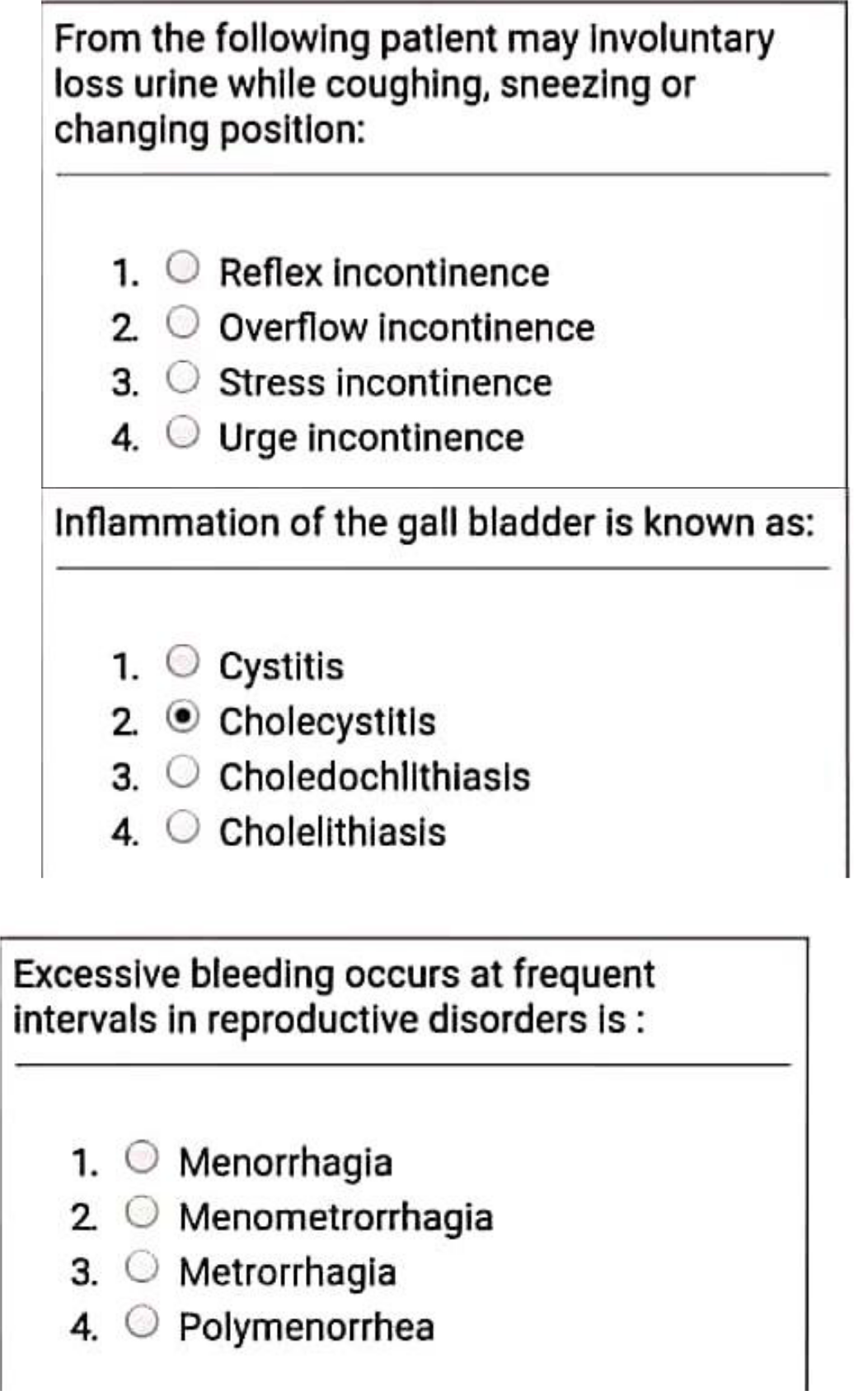
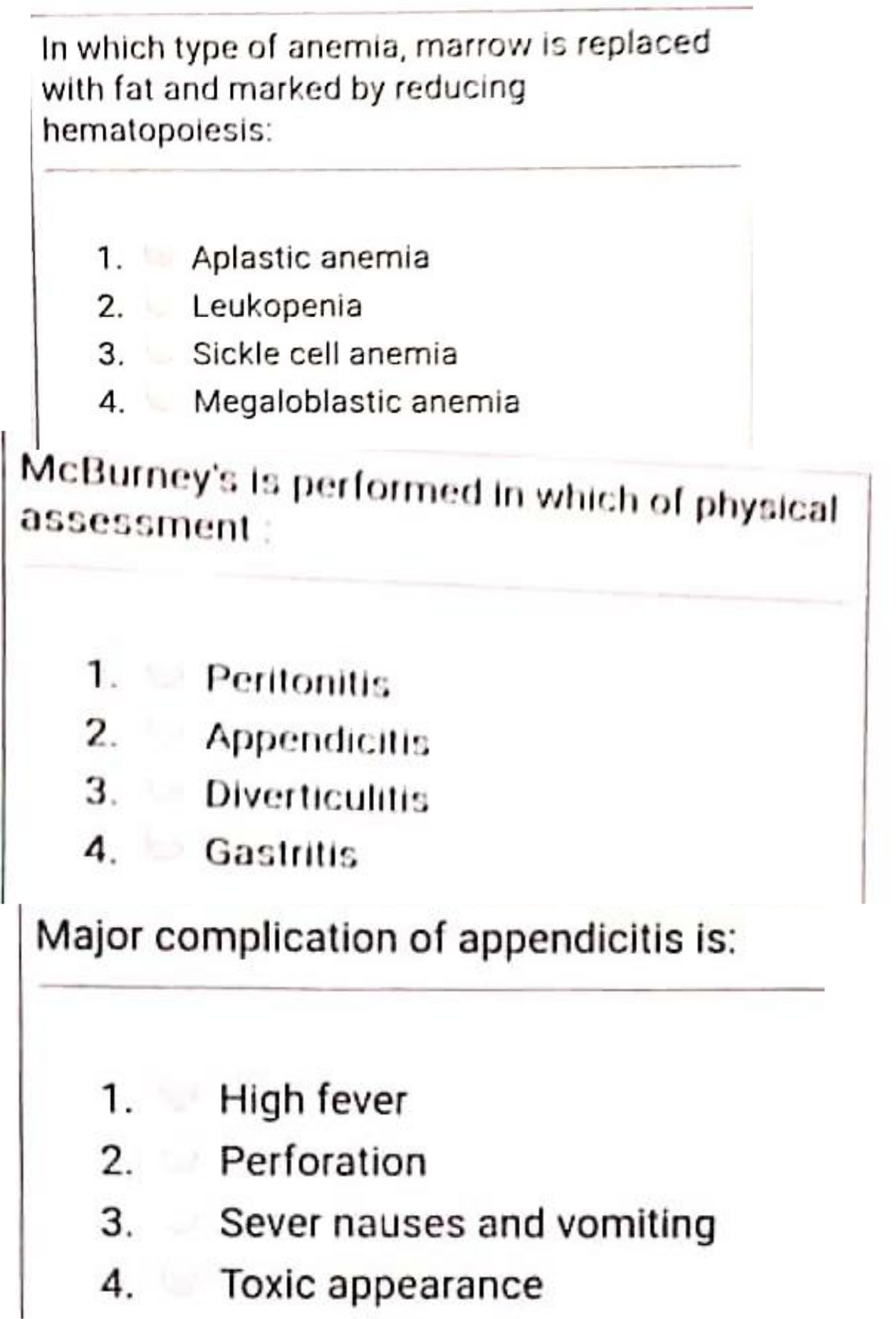
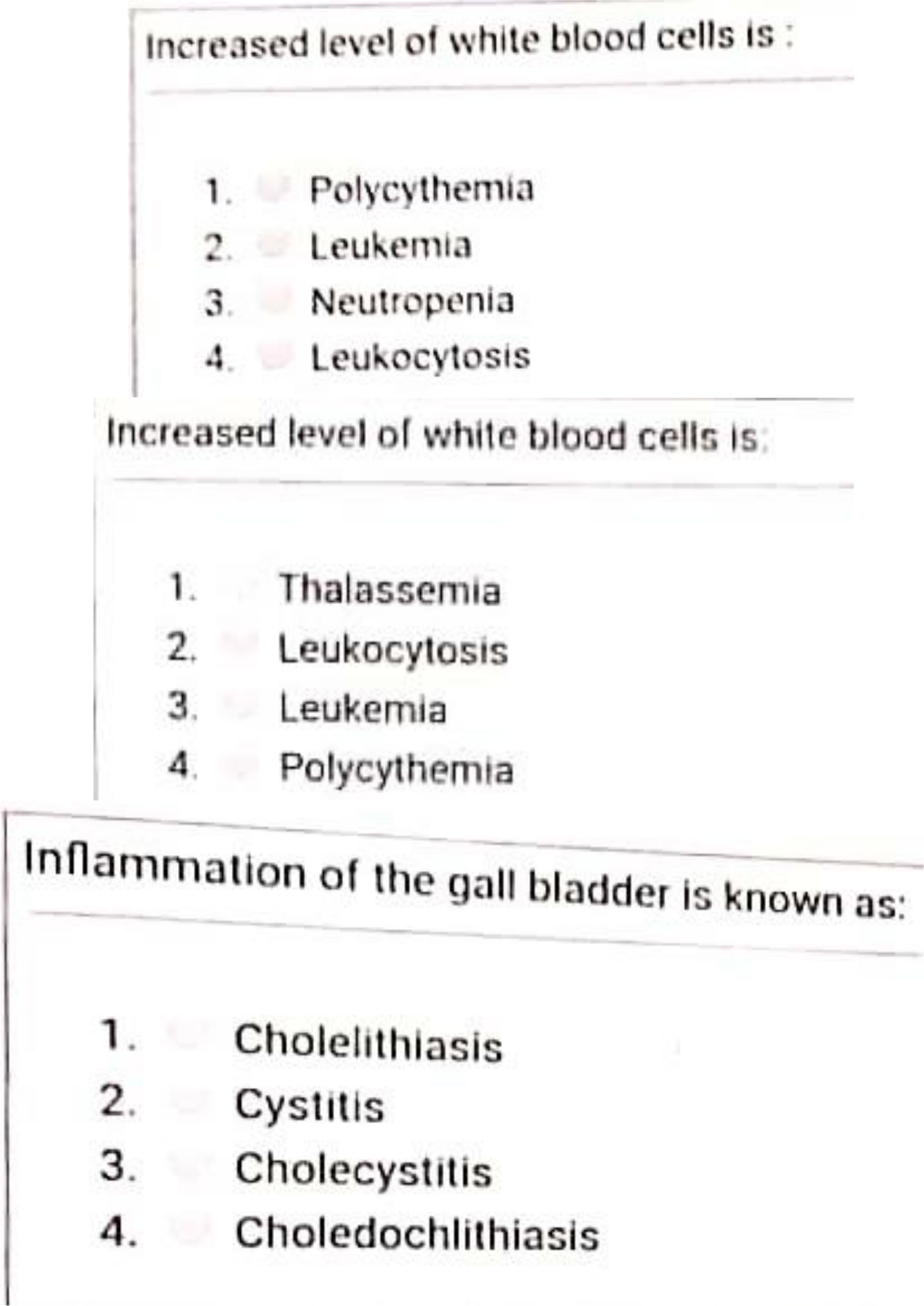
Over the past 50 years, men’s sperm count has declined by 51 percent.
This is the most important conclusion in the research conducted by Israel’s Hebrew University of Jerusalem and Mount Sinai School of Medicine in America.
Researchers analyzed the data and found that men had an average of 101 million reproductive cells per millimeter of semen in 1970, but that average has now dropped to 49 million.
As well as quantity, there is evidence that the quality of men has also declined, and reproductive cells have declined over the past decades.
“What was most affected was the sperm’s ability to circulate,” says urologist and andrologist Moker Raphael Radelli, vice president of the Razilian Association of Assisted Reproduction. Without this ability, the reproductive capacity of the sperm decreases.
Sperm count affected over time has concerned health experts.
“It’s really worrying because we’re seeing this process accelerate and we don’t even know where it’s going to end,” says Dr. Eduardo Miranda.
According to the same study, between 1970 and 1990, there was a 1.16% decline in sperm count, which has increased to 2.64% since 2000.
What is alarming is that it has become a global problem and scientists are seeing an increase in this trend across the globe.
However, the question is, what could be the reasons behind this problem? According to experts, there are five possible reasons for this. However, the good news is that there are ways to improve it.
Obesity
If you are overweight, it can affect the health of your sperm.
Obesity leads to increased growth of adipose tissue, which releases a substance that directly affects the hormone testosterone. It is the most important hormone in sperm production.
According to Miranda, obesity also increases oxidative stress, which affects cells in the body.
“Similarly, an obese person also develops obesity around the penis, which can be very dangerous for spermatozoa,” he says.
The testicles, where reproductive cells are stored, should be kept at a temperature one to two degrees cooler than the rest of the body. This is why the scrotal sac is outside the body in men.
This is the reason that due to the increase in fat, the reproductive capacity of the organs is reduced or may be completely eliminated.
According to the World Health Organization, 39% of men worldwide are overweight. This explains why the sperm count has fallen over the past decades.
Addiction
Alcohol, cigarettes, vaping ie use of electronic cigarettes, use of marijuana, cocaine and steroids. You know what all these items have in common?
All of these affect sperm count and quality in men.
“Some of these things have a direct effect on these cells, while others have an indirect effect,” says Marand. They can also affect the production of hormones that are important for testicular health.
The biggest example in this regard is the testosterone replacement drugs, gels and injections used by experts, which are usually used during bodybuilding.
According to experts, this market has expanded at an alarming rate over the years. Experts further say that when you inject this hormone into the body for no reason, the body thinks that its production is no longer needed.
This can also cause the testicles to decrease in size and the sperm count to drop. This disorder is called azoospermia.
Sexually transmitted infections
Sexually transmitted diseases that cause inflammation of the epididymis, such as chlamydia and gonorrhea, can also cause damage.
The epididymis is actually attached to the testicles and is where the sperm are stored, so any changes here can affect the sperm.
According to World Health Organization estimates, 129 million new cases of chlamydia and 82 million new cases of gonorrhea occurred in men and women in 2020.
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is also involved, says Dr. Radelli.
“It is also said to affect sperm production and even DNA,” he says.
Habit of sitting with laptop on lap
The testicles, where reproductive cells are stored, should be kept at a temperature one to two degrees cooler than the rest of the body. This is why the scrotal sac is outside the body in men.
According to research published in the last decade, the habit of keeping a laptop on one’s lap can lead to a decrease in sperm count.
Toxic substances
Experts also point to toxins commonly known as endocrine disruptors.
They are found in air pollution as well as in plastics and pesticides.
In short, the structure of these molecules is very similar to the hormones in our body. Just like a key fits into a lock, these substances manage to fit into cell receptors and trigger some unwanted process.
One of the new discoveries in recent research has been linked to reproduction, but research is still ongoing.
“But we don’t know the exact extent of the problem yet, and there’s a lot of research going on to determine that,” Radley says.
Loss of fatherhood
Besides the environmental and lifestyle factors behind low sperm count, there are two internal issues that also contribute to this phenomenon. The first of these is genetic.
An estimated 10 to 30 percent of cases of infertility are related to problems in the male’s DNA.
The second is related to aging and the fact that men’s ability to become fathers increases with age.
“We know that fertility declines throughout life,” he explains. Although the deficiency in men is not as pronounced as in women, there is a reduction in hormones that are important for the production of sperms.
If we consider that the number of sperm has declined by 51% in 50 years and the speed at which this is happening has accelerated in the last two decades, is the trend getting closer and closer to zero?
If this rate of sperm count decline continues at its current rate, by 2050 the reproductive cell concentration will be close to zero. But Miranda believes that is unlikely to happen.
According to Miranda, “The situation is deteriorating, but at some point this process will stop, perhaps with the help of new technologies.”
Methods of rescue
For those who want to have a baby, the first step to increase the chances of success is to make some changes in your lifestyle and thereby eliminate habits that are harmful to the testicles.
Examples include maintaining or losing weight through a balanced diet and regular physical exercise. Abstinence or total abstinence from alcohol, cigarettes and other drugs is also a basic requirement.
If you have recreational sex, it is important to use condoms to prevent other infections, including chlamydia.
People who are vaccinated against HPV at an early age are better protected against the virus and its effects on the body.
If despite all these changes in the routine, the difficulty in conceiving a child persists, a doctor should be consulted immediately.
According to national and international guidelines, the type of treatment will depend on the age of the woman.
“If you’re under 35, couples should try to have a baby for a year,” says Miranda.
“This process should be continued with regular intercourse about three times a week.”
However, if the couple is over 35 years of age, difficulty conceiving beyond six months is a cause for alarm.
“Research needs to involve couples to explore possible causes and identify the best treatments,” Radley says.
If the problem is in men, experts usually recommend vitamin supplements rich in antioxidants that help protect the testicles.
According to Miranda, “Certainly it is possible to correct some diseases with drugs and surgery that are at the root of the problem.”
As a last resort couples may resort to assisted reproductive techniques such as in vitro fertilization.