Key facts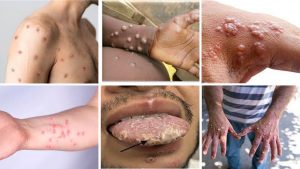
- Mpox, also called “monkeypox,” is a disease caused by a virus called the monkeypox virus, which is a species of the genus Orthopoxvirus. There are two different clades: clade I and clade II.
- Common symptoms of Monkeypox include a skin rash or mucosal lesions that can last 2–4 weeks, along with fever, headache, muscle aches, back pain, low energy, and swollen lymph nodes.
- Monkeypox can be passed to humans through direct contact with an infected person, contaminated materials, or infected animals.
- PCR tests of skin lesions can be used to prove Monkeypox in the lab.
- Supportive care is used to treat mumps. Some vaccines and treatments for smallpox that have been cleared for use in some countries can also be used for Monkeypox.
- In 2022–2023, a type called clade IIb spread Monkeypox all over the world.
- You can avoid getting Monkeypox by staying away from people who have it. Vaccinations can help keep people who are at risk from getting sick.
Overview
Mpox, also called “monkeypox,” is a condition spread by the monkeypox virus. It may cause you a fever, a painful rash, and swollen lymph nodes. The majority of people get better, but some get very sick.
Anyone can get Monkeypox. It spreads through touch with people who have it:
- Individuals, through touch, kissing, or sex;
- Animals, when shooting, skinning, or cooking them;
- Materials, such as dirty sheets, clothes, or needles;
- Pregnant individuals, who may pass the virus on to their developing child.
If you have Monkeypox:
- Tell anyone you’ve been close to recently
- Stay at home until all the scabs fall off and a new layer of skin forms
- Cover the sores and wear a mask when you’re around other people.
- Don’t touch anyone.
The monkeypox virus, also known as MPXV, is what causes Monkeypox, which used to be called monkeypox. MPXV is an enveloped double-stranded DNA virus of the Orthopoxvirus genus in the Poxviridae family. Other viruses in this family include variola, cowpox, vaccinia, and others. Clades I and II are the two groups of genes that make up the virus.
The monkeypox virus was first found in 1958 in monkeys kept for study in Denmark. In 1970, a nine-month-old boy in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) was the first person to be diagnosed with monkeypox. Mumps can be passed from person to person and sometimes from animals to people. After smallpox was wiped out in 1980 and vaccinations against it were stopped everywhere, Monkeypox slowly spread through central, east, and west Africa. In 2022 and 2023, there was a worldwide spread. No one knows where the virus comes from in nature, but small animals like squirrels and monkeys can get it.
Transmission
Person-to-person transmission of Monkeypox can happen through direct contact with infected skin or other lesions, like those in the mouth or genitals. This includes
- face-to-face contact (talking or breathing),
- skin-to-skin contact (touching or vaginal/anal sex),
- mouth-to-mouth contact (kissing), and
- mouth-to-skin contact (oral sex or kissing the skin).
- breathing drops or short-range fumes from close touch for a long time
The virus then gets into the body through broken skin, mucous areas (like the mouth, throat, eyes, genitalia, and urethra), or the breathing system. Mumps can spread to other people in the same house and to people who have sex. People who have more than one sexual partner are more likely to get sick.
People can get Monkeypox from animals when they bite or scratch them, or when they hunt, skin, trap, cook, play with dead animals, or eat them. We don’t know everything about how viruses spread through animal groups, and more research is being done.
People can get Monkeypox from infected items like clothes or sheets, from sharps injuries in health care, or in public places like tattoo parlours.
Signs and symptoms
Monkeypox causes signs and symptoms that usually start within a week, but can start anywhere from 1 to 21 days after contact. Symptoms usually last between two and four weeks, but someone with a weak immune system may have them for longer.
Common symptoms of Monkeypox are:
- rash
- fever
- sore throat
- headache
- muscle aches
- back pain
- low energy
- swollen lymph nodes.
For some people, the first sign of Monkeypox is a rash. For others, the first sign may be something else.
The rash starts out as a flat sore that turns into a blister filled with fluid. The blister may itch or hurt. As the rash gets better, the sores dry out, harden, and fall off.
Some people have one or two skin blemishes, while others have hundreds or even thousands. These can appear anywhere on the body such as the:
- palms of hands and soles of feet
- face, mouth and throat
- groin and genital areas
- anus.
Some people also have painful swelling of their rectum, or they have pain and trouble going to the toilet.
People with monkeypox are contagious and can give the disease to others until all the sores have healed and a new layer of skin has grown.
People with weak immune systems, children, and pregnant women are more likely to get sick from monkeypox.
Most of the time, heat, aches in the muscles, and a sore throat are the first signs of monkeypox. The rash of monkeypox starts on the face and moves to the rest of the body, including the palms and soles of the feet and hands. It happens in stages over 2 to 4 weeks: macules, papules, vesicles, and pustules. Lesions have a depression in the middle before they crust over. Then, the scabs fall off. Monkeypox often causes lymphadenopathy, which means that the lymph nodes swell up. Some people can be sick but not show any signs of illness.
In the setting of the worldwide spread of monkeypox that started in 2022 and was mostly caused by the Clade IIb virus, some people get sick in different ways. A rash can show up before or at the same time as other symptoms in just over half of cases, and it doesn’t always spread all over the body. The first spot can be in or around the mouth, in the groyne, or in the anus.
When someone has monkeypox, they can get very sick. For example, germs can get into the skin and cause sores or major damage to the skin. Other complications include pneumonia, an infection of the cornea that causes blindness, pain or trouble swallowing, vomiting and diarrhoea that cause severe dehydration or malnutrition, sepsis, inflammation of the brain (encephalitis), heart (myocarditis), rectum (proctitis), genital organs (balanitis), or urinary passages (urethritis), or death. Monkeypox is more likely to cause major illness or death in people whose immune systems are weak because of medicine or a medical condition. People whose HIV is not well controlled or handled are more likely to get very sick.
Diagnosis
Monkeypox can be hard to spot because it looks like other illnesses and diseases. It is important to tell the difference between monkeypox and chickenpox, measles, bacterial skin infections, lice, herpes, syphilis, and other sexually transmitted diseases, as well as allergies caused by medications. Someone with monkeypox might also have an illness that can be spread sexually, like herpes. On the other hand, a child who might have monkeypox could also have chickenpox. Because of these things, testing is important so that people can get care as soon as possible and the disease doesn’t spread further.
The best lab test for Monkeypox is polymerase chain reaction (PCR), which looks for virus DNA. The best diagnostic samples come from the rash itself—skin, fluid, or crusts—and are taken by swabbing it hard. If there are no skin sores, tests can be done with swabs from the oropharynx, the anus, or the pelvic area. It is not a good idea to test blood. Methods for finding antibodies may not be useful because they can’t tell the difference between different orthopoxviruses.
Treatment and vaccination
The goal of treating monkeypox is to get rid of the rash, ease the pain, and keep other problems from happening. It’s important to get care early and in a helpful way to help handle symptoms and keep problems from getting worse.
Getting a vaccine against monkeypox can help keep you from getting sick. The vaccine should be given within 4 days of coming into touch with someone who has monkeypox, or within 14 days if there are no signs.
People who are at a high risk of getting Monkeypox should get vaccine, especially when there is an outbreak. This includes:
- health workers at risk of exposure
- men who have sex with men
- people with multiple sex partners
- sex workers.
People who have monkeypox should be cared for away from other people.
Tecovirimat and other antivirals that were made to treat smallpox have been used to treat monkeypox, and more research is being done. There is more information about monkeypox vaccinations and how to treat cases.
Self-care and prevention
Most people get better in 2–4 weeks after getting monkeypox. Things you can do to ease the symptoms and keep from spreading the illness:
Do
- If you can, stay home and in your own room.
- Wash your hands often with soap and water or hand sanitizer, especially before or after touching sores.
- Wear a mask and cover sores when you’re around other people until your rash heals.
- Keep skin dry and covered (unless you’re in a room with someone else);
- Don’t touch things in shared spaces and clean them often;
- Rinse mouth sores with saltwater;
- Soothe body sores with sitz baths, warm baths with baking soda or Epsom salts;
- Take painkillers like paracetamol (acetaminophen) or ibuprofen.
Do not
- pop blisters or scratch sores, which can slow healing, spread the rash to other parts of the body, and cause sores to get sick; or
- shave areas with sores until scabs have healed and new skin is showing (this can spread the rash to other parts of the body).
To prevent Monkeypox from spreading to other people, those who have it should stay at home or, if necessary, in the hospital for as long as they are contagious (from the start of symptoms until sores have healed and scabs fall off). Covering the sores and wearing a medical mask when around other people may help stop the disease from spreading. Using a condom when you have sex will lower your chance of getting monkeypox, but it won’t stop the virus from spreading through skin-to-skin or mouth-to-skin contact.
Source: WHO




